Gossypol enhances ponatinib's cytotoxicity against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by involving cell cycle arrest, p-AKT/LC3II/p62, and Bcl2/caspase-3 pathways
- PMID: 39802605
- PMCID: PMC11719416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101856
Gossypol enhances ponatinib's cytotoxicity against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by involving cell cycle arrest, p-AKT/LC3II/p62, and Bcl2/caspase-3 pathways
Abstract
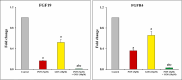
Despite significant breakthroughs in frontline cancer research and chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), many of the suggested drugs have high toxic side effects and resistance, limiting their clinical utility. Exploring potential therapeutic targets or novel combinations with fewer side effects is therefore crucial in combating this dreadful disease. The current study aims to use a novel combination of ponatinib and gossypol against the HepG2 cell line. Cell survival, FGF19/FGFR4, apoptotic and autophagic cell death, and synergistic drug interactions were assessed in response to increasing concentrations of ponatinib and/or gossypol treatment. Research revealed that ponatinib (1.25-40 μM) and gossypol (2.5-80 μM) reduced the viability of HepG2 cells in a way that was dependent on both time and dose. Ponatinib's anti-proliferation effectiveness was improved synergistically by gossypol and was associated with a rise in apoptotic cell death, cell cycle blockage during the G0/G1 phase, and suppression of the FGF19/FGFR4 axis. Furthermore, the ponatinib/gossypol combination lowered Bcl-2 and p-Akt while increasing active caspase-3, Beclin-1, p62, and LC3II. This combination, however, had no harm on normal hepatocytes. Overall, gossypol enhanced ponatinib's anticancer effects in HCC cells. Notably, this new combination appears to be potential adjuvant targeted chemotherapy, a discovery that warrants more clinical investigation, in the management of patients with HCC.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Autophagy; Cell cycle arrest; Gossypol; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Ponatinib.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures







Similar articles
-
The ponatinib/gossypol novel combination provides enhanced anticancer activity against murine solid Ehrlich carcinoma via triggering apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation/angiogenesis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 1;432:115767. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115767. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34699866
-
Chemoresistance is associated with increased cytoprotective autophagy and diminished apoptosis in bladder cancer cells treated with the BH3 mimetic (-)-Gossypol (AT-101).BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 7;15:224. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1239-4. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25885284 Free PMC article.
-
Gossypol induces cell death by activating apoptosis and autophagy in HT-29 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):2128-2132. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6804. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28656225
-
The HDAC Inhibitor Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) Supresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma alone and Synergistically in Combination with Sorafenib by G0/G1 phase arrest and Apoptosis induction.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Oct 20;14(13):1845-1858. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.27661. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30443188 Free PMC article.
-
Ponatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Leukemia: Recommendations of a German Expert Consensus Panel with Focus on Cardiovascular Management.Acta Haematol. 2020;143(3):217-231. doi: 10.1159/000501927. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Acta Haematol. 2020. PMID: 31590170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shinde S.D., Sahu B., Chamoli A., Mandoli A., Kalia K., Behera S.K. Tyrosine kinases: their role in hepatocellular carcinoma. Thera Precis. Med. Manag. Hepatocell. Carcinoma, Vol. 2: Diagn., Ther. Targets, Mol. Mech. 2022:133–148. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-98807-0.00010-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

