This is a preprint.
Autophagy-Mediated Downregulation of AXL and TIM-1 Promotes Sustained Zika Virus Infection
- PMID: 39803534
- PMCID: PMC11722360
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.31.630961
Autophagy-Mediated Downregulation of AXL and TIM-1 Promotes Sustained Zika Virus Infection
Update in
-
Autophagy-mediated downregulation of AXL and TIM-1 promotes sustained Zika virus infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 27;122(21):e2427241122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2427241122. Epub 2025 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40408405 Free PMC article.
Abstract
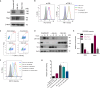
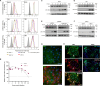
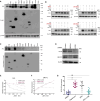
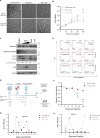
Zika virus (ZIKV) infection can lead to a variety of clinical outcomes, including severe congenital abnormalities. The phosphatidylserine (PS) receptors AXL and TIM-1 are recognized as critical entry factors for ZIKV in vitro. However, it remains unclear if and how ZIKV regulates these receptors during infection. In this study, we investigated AXL and TIM-1 expression in human alveolar basal epithelial A549 cells, glioblastoma U87 cells, and embryonic stem cells-derived trophoblast following ZIKV infection. We found that both the Asian strain FSS13025 and the African strain MR766 of ZIKV downregulate AXL, with a milder effect on TIM-1. We identified several ZIKV proteins, notably envelope (E), NS2A, NS3, and NS4B, that contribute to this downregulation. Notably, treatment with lysosomal inhibitor NH4Cl or the autophagy inhibitor 3-Methyladenine (3-MA) mitigated the AXL/TIM-1 downregulation, indicating autophagy's involvement in the process. Importantly, this downregulation facilitates sustained viral replication and promotes viral spread by preventing superinfection and limiting cell death, which is also associated with impaired innate immune signaling. Our findings uncover a mechanism by which ZIKV downregulates entry factors to enhance prolonged viral replication and spread.
Keywords: AXL; Autophagy; Down-Regulation; TIM-1; ZIKV.
Figures
References
-
- Honein M. A. et al. , Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Evidence of Possible Zika Virus Infection During Pregnancy. JAMA 317, 59–68 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Santos T. d. et al. , Zika Virus and the Guillain–Barré Syndrome — Case Series from Seven Countries. New England Journal of Medicine 375, 1598–1601 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Pierson T. C., Diamond M. S., The emergence of Zika virus and its new clinical syndromes. Nature 560, 573–581 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
