Identification of novel PfEMP1 variants containing domain cassettes 11, 15 and 8 that mediate the Plasmodium falciparum virulence-associated rosetting phenotype
- PMID: 39804943
- PMCID: PMC11759366
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012434
Identification of novel PfEMP1 variants containing domain cassettes 11, 15 and 8 that mediate the Plasmodium falciparum virulence-associated rosetting phenotype
Abstract
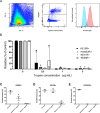
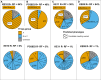
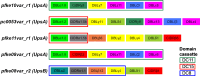
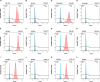
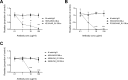
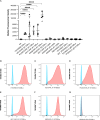
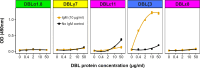
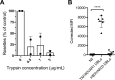
Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) is a diverse family of variant surface antigens, encoded by var genes, that mediates binding of infected erythrocytes to human cells and plays a key role in parasite immune evasion and malaria pathology. The increased availability of parasite genome sequence data has revolutionised the study of PfEMP1 diversity across multiple P. falciparum isolates. However, making functional sense of genomic data relies on the ability to infer binding phenotype from var gene sequence. For P. falciparum rosetting, the binding of infected erythrocytes to uninfected erythrocytes, the analysis of var gene/PfEMP1 sequences encoding the phenotype is limited, with only eight rosette-mediating PfEMP1 variants described to date. These known rosetting PfEMP1 variants fall into two types, characterised by N-terminal domains known as "domain cassette" 11 (DC11) and DC16. Here we test the hypothesis that DC11 and DC16 are the only PfEMP1 types in the P. falciparum genome that mediate rosetting, by examining a set of thirteen recent culture-adapted Kenyan parasite lines. We first analysed the var gene/PfEMP1 repertoires of the Kenyan lines and identified an average of three DC11 or DC16 PfEMP1 variants per genotype. In vitro rosette selection of the parasite lines yielded four with a high rosette frequency, and analysis of their var gene transcription, infected erythrocyte PfEMP1 surface expression, rosette disruption and erythrocyte binding function identified four novel rosette-mediating PfEMP1 variants. Two of these were of the predicted DC11 type (one showing the dual rosetting/IgM-Fc-binding phenotype), whereas two contained DC15 (DBLα1.2-CIDRα1.5b) a PfEMP1 type not previously associated with rosetting. We also showed that a Thai parasite line expressing a DC8-like PfEMP1 binds to erythrocytes to form rosettes. Hence, these data expand current knowledge of rosetting mechanisms and emphasize that the PfEMP1 types mediating rosetting are more diverse than previously recognised.
Copyright: © 2025 McLean et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunisation with recombinant PfEMP1 domains elicits functional rosette-inhibiting and phagocytosis-inducing antibodies to Plasmodium falciparum.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 31;6(1):e16414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016414. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21305024 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of the Plasmodium falciparum PfEMP1-VarO Adhesin: Induction of Surface-Reactive and Rosette-Disrupting Antibodies to VarO Infected Erythrocytes.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0134292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134292. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222304 Free PMC article.
-
α2-Macroglobulin Can Crosslink Multiple Plasmodium falciparum Erythrocyte Membrane Protein 1 (PfEMP1) Molecules and May Facilitate Adhesion of Parasitized Erythrocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jul 2;11(7):e1005022. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005022. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26134405 Free PMC article.
-
Three Is a Crowd - New Insights into Rosetting in Plasmodium falciparum.Trends Parasitol. 2017 Apr;33(4):309-320. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.12.012. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Trends Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28109696 Review.
-
Malaria's deadly grip: cytoadhesion of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes.Cell Microbiol. 2013 Dec;15(12):1976-83. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12183. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Cell Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23957661 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

