Traditional Chinese Medicine Borneol-Based Polymeric Micelles Intracerebral Drug Delivery System for Precisely Pathogenesis-Adaptive Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 39804950
- PMCID: PMC11884575
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202410889
Traditional Chinese Medicine Borneol-Based Polymeric Micelles Intracerebral Drug Delivery System for Precisely Pathogenesis-Adaptive Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
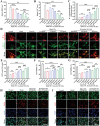
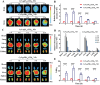
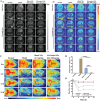
The scarcity of effective neuroprotective agents and the presence of blood-brain barrier (BBB)-mediated extremely inefficient intracerebral drug delivery are predominant obstacles to the treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke (CIS). Herein, ROS-responsive borneol-based amphiphilic polymeric NPs are constructed by using traditional Chinese medicine borneol as functional blocks that served as surface brain-targeting ligand, inner hydrophobic core for efficient drug loading of membrane-permeable calcium chelator BAPTA-AM, and neuroprotective structural component. In MCAO mice, the nanoformulation (polymer: 3.2 mg·kg-1, BAPTA-AM: 400 µg·kg-1) reversibly opened the BBB and achieved high brain biodistribution up to 12.7%ID/g of the total administered dose after 3 h post single injection, effectively restoring intracellular Ca2+ and redox homeostasis, improving cerebral histopathology, and inhibiting mitochondrial PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2/Bax/Cyto-C/Caspase-3,9 apoptosis pathway for rescuing dying neurons (reduced apoptosis cell from 59.5% to 7.9%). It also remodeled the inflammatory microenvironment in cerebral ischemic penumbra by inhibiting astrocyte over-activation, reprogramming microglia polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype, and blocking NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6 signaling pathways. These interventions eventually reduced the cerebral infarction area by 96.3%, significantly improved neurological function, and restored blood flow reperfusion from 66.2% to ≈100%, all while facilitating BBB repair and avoiding brain edema. This provides a potentially effective multiple-stage sequential treatment strategy for clinical CIS.
Keywords: BAPTA‐AM; ROS‐responsive; blood‐brain barrier; borneol; ischemic stroke.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
The protective effects of Axitinib on blood-brain barrier dysfunction and ischemia-reperfusion injury in acute ischemic stroke.Exp Neurol. 2024 Sep;379:114870. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114870. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38897539
-
l-Borneol ameliorates cerebral ischaemia by downregulating the mitochondrial calcium uniporter-induced apoptosis cascade in pMCAO rats.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 4;73(2):272-280. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgaa028. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33793797
-
Sanhua Tang protects against ischemic stroke by preventing blood-brain barrier injury: a network pharmacology and experiments.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Aug;44(4):794-803. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240515.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39066540 Free PMC article.
-
Borneol for Regulating the Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Experimental Ischemic Stroke: Preclinical Evidence and Possible Mechanism.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Feb 4;2019:2936737. doi: 10.1155/2019/2936737. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 30863478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric nanocarriers delivery systems in ischemic stroke for targeted therapeutic strategies.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 18;22(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02673-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39026255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Piezo1 disrupts blood-brain barrier via CaMKII/Nrf2 in ischemic stroke.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jun 28;82(1):259. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05804-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40579608 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of astrocytes in the blood-brain barrier during the acute and recovery phases of stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Apr 1;21(4):1359-1372. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01417. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40537147 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient brain delivery system co-loaded with multiple components of Salvia miltiorrhiza for synergistic treatment of ischemic stroke.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 16;34:102102. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102102. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40747116 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- tsqn202211065/Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province
- zrjj-134-jch/Natural Science Foundation of Qingdao City of China
- 2021JJLH0037/Hainan Provincial Joint Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City
- ZDYF2024SHFZ056/Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund
- 202461020/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
