Defining proteoform-specific interactions for drug targeting in a native cell signalling environment
- PMID: 39806141
- PMCID: PMC11794133
- DOI: 10.1038/s41557-024-01711-w
Defining proteoform-specific interactions for drug targeting in a native cell signalling environment
Abstract
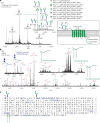
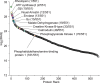
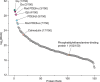
Understanding the dynamics of membrane protein-ligand interactions within a native lipid bilayer is a major goal for drug discovery. Typically, cell-based assays are used, however, they are often blind to the effects of protein modifications. In this study, using the archetypal G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin, we found that the receptor and its effectors can be released directly from retina rod disc membranes using infrared irradiation in a mass spectrometer. Subsequent isolation and dissociation by infrared multiphoton dissociation enabled the sequencing of individual retina proteoforms. Specifically, we categorized distinct proteoforms of rhodopsin, localized labile palmitoylations, discovered a Gβγ proteoform that abolishes membrane association and defined lipid modifications on G proteins that influence their assembly. Given reports of undesirable side-effects involving vision, we characterized the off-target drug binding of two phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, vardenafil and sildenafil, to the retina rod phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6). The results demonstrate differential off-target reactivity with PDE6 and an interaction preference for lipidated proteoforms of G proteins. In summary, this study highlights the opportunities for probing proteoform-ligand interactions within natural membrane environments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.L.B., D.W., S.A.B. and W.B.S. declare no competing interests. I.L. is an employee of OMass Therapeutics. C.V.R. is a consultant of OMass Therapeutics. J.D.H., C.M. and J.E.P.S. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific and are Research and Development Scientists in the life sciences mass spectrometry business. C.A.L., T.J.E., C.V.R., I.L., J.D.H. and J.E.P.S. are inventors on a UK patent application (GB2215982.6) that describes the infrared liberation of membrane proteins from native bilayers for top-down analysis method reported in this paper.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

