Intramolecular Agostic Interactions and Dynamics of a Methyl Group at a Preorganized Dinickel(II) Site
- PMID: 39807790
- PMCID: PMC11776048
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c04255
Intramolecular Agostic Interactions and Dynamics of a Methyl Group at a Preorganized Dinickel(II) Site
Abstract
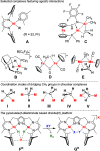
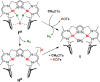
Alkyl nickel intermediates relevant to catalytic processes often feature agostic stabilization, but relatively little is known about the situation in oligonickel systems. The dinickel(I) complex K[LNiI2], which is based on a compartmental pyrazolato-bridged ligand L3- with two β-diketiminato chelate arms, or its masked version, the dihydride complex [KL(NiII-H)2] that readily releases H2, oxidatively add methyl tosylate to give diamagnetic [LNiII2(CH3)] (1) with d(Ni···Ni) ≈ 3.7 Å. Structural characterization shows that the methyl group in 1 is bound to one NiII and exhibits an intramolecular agostic interaction with the more distant NiII. This is supported spectroscopically (viz., a ν(C-H) stretch at 2658 cm-1 and lowered 1JC-H of 114 Hz) and by DFT calculations, including topological analysis of the computed electron density for 1. NMR spectroscopy reveals very fast hopping of the CH3 group between the two NiII ions, which according to DFT has a minute barrier of 4 kcal mol-1 and proceeds via a planar CH3 moiety in the transition state (Walden-like inversion). The alkylidene group in K[LNi2(μ-CHSi(Me3)3)], obtained from the reaction of [KL(Ni-H)2] with N2CHSiMe3, is symmetrically bridging. This work provides new insight into the stabilization and dynamics of alkyl ligands at dinickel sites with a constrained metal···metal distance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







References
-
-
See, for example:
- Leatherman M. D.; Svejda S. A.; Johnson L. K.; Brookhart M. Mechanistic Studies of Nickel(II) Alkyl Agostic Cations and Alkyl Ethylene Complexes: Investigations of Chain Propagation and Isomerization in (α-diimine)Ni(II)-Catalyzed Ethylene Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3068–3081. 10.1021/ja021071w. - DOI - PubMed
- Mitoraj M. P.; Michalak A.; Ziegler T. On the Nature of the Agostic Bond between Metal Centers and β-Hydrogen Atoms in Alkyl Complexes. An Analysis Based on the Extended Transition State Method and the Natural Orbitals for Chemical Valence Scheme (ETS-NOCV). Organometallics 2009, 28, 3727–3733. 10.1021/om900203m. - DOI
- Diccianni J.; Lin Q.; Diao T. Mechanisms of Nickel-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions and Applications in Alkene Functionalization. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 906–919. 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
-
- Conroy-Lewis F. M.; Mole L.; Redhouse A. D.; Litster S. A.; Spencer J. L. Synthesis of Coordinatively Unsaturated Diphosphine Nickel(II) and Palladium(II) P-Agostic Ethyl Cations: X-Ray Crystal Structure of [Ni{But2P(CH2)2PBUt2}(C2H5)][BF4]. Chem. Commun. 1991, 1601–1603. 10.1039/C39910001601. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

