New Directions for Ophthalmic OCT - Handhelds, Surgery, and Robotics
- PMID: 39808124
- PMCID: PMC11737465
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.14.1.14
New Directions for Ophthalmic OCT - Handhelds, Surgery, and Robotics
Abstract
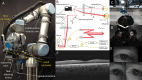
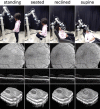
The introduction of optical coherence tomography (OCT) in the 1990s revolutionized diagnostic ophthalmic imaging. Initially, OCT's role was primarily in the adult ambulatory ophthalmic clinics. Subsequent advances in handheld form factors, integration into surgical microscopes, and robotic assistance have expanded OCT's utility and impact outside of its initial environment in the adult outpatient ophthalmic clinic. In this review, we cover the use of OCT in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) environment with a handheld OCT, recent developments in intraoperative OCT for data visualization and measurements, and recent work and demonstration of robotically aligned OCT systems outside of eye clinics. Of note, advances in these areas are a legacy of our colleague, the late Joseph Izatt. OCT has been an important innovation for ocular diagnostics, and these advances have helped it continue to extend in new directions.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures





References
-
- Swanson EA, Izatt JA, Hee MR, et al. .. In vivo retinal imaging by optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 1993; 18: 1864–1866. - PubMed
-
- Izatt JA, Hee MR, Swanson EA, et al. .. Micrometer-scale resolution imaging of the anterior eye in vivo with optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994; 112: 1584–1589. - PubMed
-
- Schuman JS, Hee MR, Arya AV, et al. .. Optical coherence tomography: a new tool for glaucoma diagnosis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995; 6: 89–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

