Electronic Patient-Reported Outcome System Implementation in Outpatient Cardiovascular Care: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 39808432
- PMCID: PMC11733702
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.54084
Electronic Patient-Reported Outcome System Implementation in Outpatient Cardiovascular Care: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: The integration of patient-reported outcome (PRO) assessments in cardiovascular care has encountered considerable obstacles despite their established clinical relevance.
Objective: To assess the impact of a physician- and patient-friendly electronic PRO (ePRO) monitoring system on the quality of cardiovascular care in clinical practice.
Design, setting, and participants: This open-label, multicenter, pilot randomized clinical trial was phase 2 of a multiphase study that was conducted from October 2022 to October 2023 and focused on the implementation and evaluation of an ePRO monitoring system in outpatient clinics in Japan. During phase 1 (conducted from December 2021 to March 2022), this ePRO monitoring system was developed at a single outpatient center using feedback from patients and physicians. Eligible patients were older than 18 years with a clinical diagnosis of heart failure (HF), atrial fibrillation (AF), or coronary artery disease (CAD). Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to either the ePRO or control group. Statistical analysis was based on the intention-to-treat approach.
Intervention: Patients in the ePRO group were asked to complete the 12-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ-12), Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life Questionnaire (AFEQT), or Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ) on smart tablets before their clinical examination. Results were reviewed by physicians at each outpatient visit. The control group received usual care consisting of medication management, lifestyle modification, and invasive procedures in accordance with clinical guidelines. Both groups had 5 monthly outpatient visits.
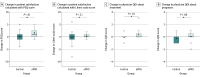
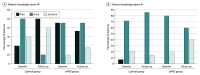
Main outcomes and measures: Patient satisfaction, quality of information (QOI) provided by physicians, and disease knowledge were assessed using questionnaires (eg, Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire [PSQ]; score range: 5-25, with higher scores indicating greater patient satisfaction) at baseline and the fifth visit, over approximately 4 months.
Results: Of the 50 patients included, 48 (median [SD] age, 71.0 [62.3-75.0] years; 28 males [58.3%]) completed follow-up. The prevalence was 56.2% (n = 27) for HF, 75.0% (n = 36) for AF, and 10.4% (n = 5) for CAD. The distribution of PRO measures used was 21 patients (43.8%) for KCCQ-12, 24 (50.0%) for AFEQT, and 3 (6.2%) for SAQ. Compared with the control group, the ePRO group showed significant improvements in mean (SD) PSQ score (0.16 [2.06] vs 1.61 [1.75]; P = .01) and QOI score regarding treatment (-0.12 [0.53] vs 0.35 [0.71]; P = .01). The ePRO group exhibited a greater increase in the PSQ score regarding communication (-0.12 [0.53] vs 0.43 [0.90]; P = .01).
Conclusions and relevance: In this randomized clinical trial, implementation of the ePRO monitoring system significantly enhanced patient-physician communication and the clarity of physicians' explanations about treatment. These findings suggest that the ePRO monitoring system is capable of supporting patient-centered cardiovascular care.
Trial registration: University Hospital Medical Information Network Identifier: UMIN000049251.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Walsh MN, Bove AA, Cross RR, et al. ; American College of Cardiology Foundation . ACCF 2012 health policy statement on patient-centered care in cardiovascular medicine: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Clinical Quality Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(23):2125-2143. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2012.03.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rumsfeld JS, Alexander KP, Goff DC Jr, et al. ; American Heart Association Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and Stroke Council . Cardiovascular health: the importance of measuring patient-reported health status: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(22):2233-2249. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182949a2e - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

