Cognitive impairment caused by compromised hepatic ketogenesis is prevented by endurance exercise
- PMID: 39808588
- PMCID: PMC12441108
- DOI: 10.1113/JP287573
Cognitive impairment caused by compromised hepatic ketogenesis is prevented by endurance exercise
Abstract
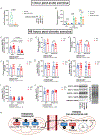
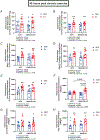
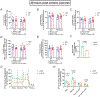
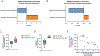
Extensive research has demonstrated endurance exercise to be neuroprotective. Whether these neuroprotective benefits are mediated, in part, by hepatic ketone production remains unclear. To investigate the role of hepatic ketone production on brain health during exercise, healthy 6-month-old female rats underwent viral knockdown of the rate-limiting enzyme in the liver that catalyses the first reaction in ketogenesis: 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2). Rats were then subjected to either a bout of acute exercise or 4 weeks of chronic treadmill running (5 days/week) and cognitive behavioural testing. Acute exercise elevated ketone plasma concentration 1 h following exercise. Hepatic HMGCS2 knockdown, verified by protein expression, reduced ketone plasma concentration 1 h after acute exercise and 48 h after chronic exercise. Proteomic analysis and enrichment of the frontal cortex revealed hepatic HMGCS2 knockdown reduced markers of mitochondrial function 1 h after acute exercise. HMGCS2 knockdown significantly reduced state 3 complex I + II respiration in isolated mitochondria from the frontal cortex after chronic exercise. Spatial memory and protein markers of synaptic plasticity were significantly reduced by HMGCS2 knockdown. These deficiencies were prevented by chronic endurance exercise training. In summary, these are the first data to propose that hepatic ketogenesis is required to maintain cognition and mitochondrial function, irrespective of training status, and that endurance exercise can overcome neuropathology caused by insufficient hepatic ketogenesis. These results establish a mechanistic link between liver and brain health that enhance our understanding of how peripheral tissue metabolism influences brain health. KEY POINTS: Decades of literature demonstrate endurance exercise to be neuroprotective. Whether neuroprotective benefits are mediated, in part, by hepatic ketone production remains unclear. This study provides the first set of data that suggest hepatic ketogenesis is required to maintain cognition, synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial function. These data indicate endurance exercise can protect against cognitive decline caused by compromised hepatic ketogenesis. These results establish a mechanistic link between liver and brain function, prompting further investigation of how hepatic metabolism influences brain health.
Keywords: HMGCS2; cerebral cortex; cognitio; exercise; ketogenesis; liver; mitochondria; proteomics.
© 2025 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2025 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Amar D, Gay NR, Jimenez-Morales D, Jean Beltran PM, Ramaker ME, Raja AN, Zhao B, Sun Y, Marwaha S, Gaul DA, Hershman SG, Ferrasse A, Xia A, Lanza I, Fernández FM, Montgomery SB, Hevener AL, Ashley EA, Walsh MJ, … Zhen J (2024). The mitochondrial multi-omic response to exercise training across rat tissues. Cell metabolism, 36(6), 1411–1429.e10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batalha VL, Ferreira DG, Coelho JE, Valadas JS, Gomes R, Temido-Ferreira M, Shmidt T, Baqi Y, Buée L, Müller CE, Hamdane M, Outeiro TF, Bader M, Meijsing SH, Sadri-Vakili G, Blum D, & Lopes LV (2016). The caffeine-binding adenosine A2A receptor induces age-like HPA-axis dysfunction by targeting glucocorticoid receptor function. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 31493. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, & Collingridge GL (1993). A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature, 361(6407), 31–39. - PubMed
-
- Bulthuis EP, Adjobo-Hermans MJW, de Potter B, Hoogstraten S, Wezendonk LHT, Tutakhel OAZ, Wintjes LT, van den Heuvel B, Willems P, Kamsteeg EJ, Gozalbo MER, Sallevelt S, Koudijs SM, Nicolai J, de Bie CI, Hoogendijk JE, Koopman WJH, & Rodenburg RJ (2023). SMDT1 variants impair EMRE-mediated mitochondrial calcium uptake in patients with muscle involvement. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, 1869(8), 166808. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
