The effect of green tea on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 39809182
- PMCID: PMC11596636
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039702
The effect of green tea on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To systematically evaluate the effect of green tea on patients with type 2 diabetes.
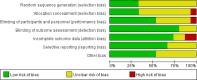
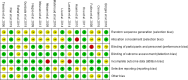
Methods: A computer search Cochrane, PubMed, Embase, CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, and other Chinese and English databases were conducted for randomized controlled trials of green tea in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. The duration of these trials spanned from the establishment of the database to January 10, 2024. The obtained data were subjected to meta-analysis using Stata15.1 software. A total of 15 articles were included, encompassing 722 patients.
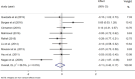
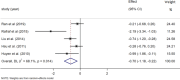
Results: The meta-analysis results showed that compared to the control group, green tea intervention significantly improved the improvement of fasting blood glucose (SMD = -0.41, 95% CI: -0.67 to -0.19, P = .001), glycated hemoglobin (SMD = -0.68, 95% CI: -1.15 to 0.21, P = .004) and insulin resistance index (SMD = -0.70, 95% CI: -1.18 to -0.22, P = .005) in the experimental group compared to the control group. The differences were statistically significant (P < .05).
Conclusion: Green tea significantly improves fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Yajie Z, Guifen F, Xiang L, et al. Investigation of the occurrence of combined sarcopenia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and analysis of influencing factors. China Clin New Med. 2023;16:1298–302.
-
- Li ZY, Fang JW, Lin KC. Analysis and prediction of the burden of disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus attributable to high body mass index in China, 1990-2019. Chin Family Med. 2024;27:1126–1133+1148.
-
- Hu RS, Zhang C, Chen YX. Research on the evaluation of the effect of non-pharmacologic intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Jilin Med. 2018;39:2166–7.
-
- Int J Epidemiol. Drinking green tea may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Mod Hosp. 2018;18:1760.
-
- Jia-Liang S, Chao-Feng W, Zhen-Liang S, et al. Comparative study of guava tea and green tea in treating female middle-aged and elderly patients with prediabetes. Shanxi Med J. 2019;48:1690–2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

