Force Nanoscopy Demonstrates Stress-Activated Adhesion between Staphylococcus aureus Iron-Regulated Surface Determinant Protein B and Host Toll-like Receptor 4
- PMID: 39810370
- PMCID: PMC11752402
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c12648
Force Nanoscopy Demonstrates Stress-Activated Adhesion between Staphylococcus aureus Iron-Regulated Surface Determinant Protein B and Host Toll-like Receptor 4
Abstract
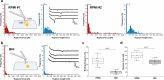
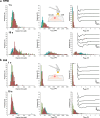
The Staphylococcus aureus iron-regulated surface determinant protein B (IsdB) has recently been shown to bind to toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), thereby inducing a strong inflammatory response in innate immune cells. Currently, two unsolved questions are (i) What is the molecular mechanism of the IsdB-TLR4 interaction? and (ii) Does it also play a role in nonimmune systems? Here, we use single-molecule experiments to demonstrate that IsdB binds TLR4 with both weak and extremely strong forces and that the mechanostability of the molecular complex is dramatically increased by physical stress, sustaining forces up to 2000 pN, at a loading rate of 105 pN/s. We also show that TLR4 binding by IsdB mediates time-dependent bacterial adhesion to endothelial cells, pointing to the role of this bond in cell invasion. Our findings point to a function for IsdB in pathogen-host interactions, that is, mediating strong bacterial adhesion to host endothelial cells under fluid shear stress, unknown until now. In nanomedicine, this stress-dependent adhesion represents a potential target for innovative therapeutics against S. aureus-resistant strains.
Keywords: IsdB; Staphylococcus aureus; TLR4; bacterial adhesion; endothelial cells; single-cell force spectroscopy; single-molecule force spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The iron-regulated surface determinant B (IsdB) protein from Staphylococcus aureus acts as a receptor for the host protein vitronectin.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 17;295(29):10008-10022. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013510. Epub 2020 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32499371 Free PMC article.
-
Force-Induced Strengthening of the Interaction between Staphylococcus aureus Clumping Factor B and Loricrin.mBio. 2017 Dec 5;8(6):e01748-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01748-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29208742 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 sensing of IsdB of Staphylococcus aureus induces a proinflammatory cytokine response via the NLRP3-caspase-1 inflammasome cascade.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0022523. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00225-23. Epub 2023 Dec 19. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38112465 Free PMC article.
-
Nanonewton forces between Staphylococcus aureus surface protein IsdB and vitronectin.Nanoscale Adv. 2020 Oct 30;2(12):5728-5736. doi: 10.1039/d0na00636j. eCollection 2020 Dec 15. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. PMID: 36133863 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Molecule Analysis Demonstrates Stress-Enhanced Binding between Staphylococcus aureus Surface Protein IsdB and Host Cell Integrins.Nano Lett. 2020 Dec 9;20(12):8919-8925. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04015. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 33237786
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

