Evaluating the effect of denoising submillimeter auditory fMRI data with NORDIC
- PMID: 39810817
- PMCID: PMC11726685
- DOI: 10.1162/imag_a_00270
Evaluating the effect of denoising submillimeter auditory fMRI data with NORDIC
Abstract
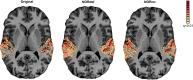
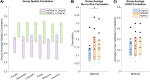
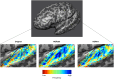
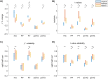
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has emerged as an essential tool for exploring human brain function. Submillimeter fMRI, in particular, has emerged as a tool to study mesoscopic computations. The inherently low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at submillimeter resolutions warrants the use of denoising approaches tailored at reducing thermal noise-the dominant contributing noise component in high-resolution fMRI. NOise Reduction with DIstribution Corrected Principal Component Analysis (NORDIC PCA) is one of such approaches, and has been benchmarked against other approaches in several applications. Here, we investigate the effects that two versions of NORDIC denoising have on auditory submillimeter data. While investigating auditory functional responses poses unique challenges, we anticipated NORDIC to have a positive impact on the data on the basis of previous applications. Our results show that NORDIC denoising improves the detection sensitivity and the reliability of estimates in submillimeter auditory fMRI data. These effects can be explained by the reduction of the noise-induced signal variability. However, we did observe a reduction in the average response amplitude (percent signal change) within regions of interest, which may suggest that a portion of the signal of interest, which could not be distinguished from general i.i.d. noise, was also removed. We conclude that, while evaluating the effects of the signal reduction induced by NORDIC may be necessary for each application, using NORDIC in high-resolution auditory fMRI studies may be advantageous because of the large reduction in variability of the estimated responses.
Keywords: NORDIC; auditory neuroscience; denoising; fMRI; high-resolution.
© 2024 The Authors. Published under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
Conflict of interest statement
NORDIC and NIFTI_NORDIC are copyrighted by Regents of the University of Minnesota and covered by issued US patent #10,768,260, and S.M. has a relationship with this patent. S.M. did not evaluate or analyze any of the data in this work.
Figures

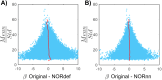

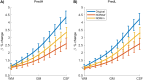
Update of
-
Evaluating the effect of denoising submillimeter auditory fMRI data with NORDIC.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 25:2024.01.24.577070. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.24.577070. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Aug 14;2:1-18. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00270. PMID: 38328173 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ahveninen , J. , Chang , W.-T. , Huang , S. , Keil , B. , Kopco , N. , Rossi , S. , Bonmassar , G. , Witzel , T. , & Polimeni , J. R. ( 2016. ). Intracortical depth analyses of frequency-sensitive regions of human auditory cortex using 7T fMRI . NeuroImage , 143 , 116 – 127 . 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen , E. J. , St-Yves , G. , Wu , Y. , Breedlove , J. L. , Prince , J. S. , Dowdle , L. T. , Nau , M. , Caron , B. , Pestilli , F. , Charest , I. , Hutchinson , J. B. , Naselaris , T. , & Kay , K. ( 2022. ). A massive 7T fMRI dataset to bridge cognitive neuroscience and artificial intelligence . Nature Neuroscience , 25 ( 1 ), 116 – 126 . 10.1038/s41593-021-00962-x - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
