Multi-target-directed therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease: controlling amyloid-β aggregation, metal ion homeostasis, and enzyme inhibition
- PMID: 39810997
- PMCID: PMC11726323
- DOI: 10.1039/d4sc06762b
Multi-target-directed therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease: controlling amyloid-β aggregation, metal ion homeostasis, and enzyme inhibition
Abstract
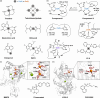
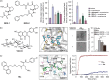
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative dementia, marked by progressive cognitive decline and memory impairment. Despite advances in therapeutic research, single-target-directed treatments often fall short in addressing the complex, multifactorial nature of AD. This arises from various pathological features, including amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregate deposition, metal ion dysregulation, oxidative stress, impaired neurotransmission, neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuronal cell death. This review illustrates their interrelationships, with a particular emphasis on the interplay among Aβ, metal ions, and AD-related enzymes, such as β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and monoamine oxidase B (MAOB). We further underscore the potential of therapeutic strategies that simultaneously inhibit Aβ aggregation and address other pathogenic mechanisms. These approaches offer a more comprehensive and effective method for combating AD, overcoming the limitations of conventional therapies.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Mechanistic Insight into the Design of Chemical Tools to Control Multiple Pathogenic Features in Alzheimer's Disease.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Oct 19;54(20):3930-3940. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00457. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34606227 Review.
-
A Novel Multifunctional 5,6-Dimethoxy-Indanone-Chalcone-Carbamate Hybrids Alleviates Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer's Disease by Dual Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and Inflammation.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 4;14:922650. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.922650. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35860673 Free PMC article.
-
Flavanone glycosides inhibit β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 and cholinesterase and reduce Aβ aggregation in the amyloidogenic pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Aug 25;309:108707. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.06.020. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31194956
-
Inhibition of BACE1, MAO-B, cholinesterase enzymes, and anti-amyloidogenic potential of selected natural phytoconstituents: Multi-target-directed ligand approach.J Food Biochem. 2021 Jan;45(1):e13571. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13571. Epub 2020 Nov 29. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33249607
-
A Recent Update on Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Interventions of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(43):3428-3441. doi: 10.2174/0113816128264355231121064704. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 38038007 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoid carbamate hybrids: design, synthesis, and evaluation as multi-target enzyme inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease.RSC Adv. 2025 May 20;15(21):16855-16868. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02267c. eCollection 2025 May 15. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40395797 Free PMC article.
-
Iron-Mediated Overexpression of Amyloid Precursor Protein via Iron Responsive mRNA in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 30;26(11):5283. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115283. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Neuroprotective Properties of Celery (Apium graveolens Linn) Extract Against Amyloid-Beta Toxicity and Enzymes Associated with Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2025 May 16;30(10):2187. doi: 10.3390/molecules30102187. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40430359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen P. H. Ramamoorthy A. Sahoo B. R. Zheng J. Faller P. Straub J. E. Dominguez L. Shea J.-E. Dokholyan N. V. De Simone A. Ma B. Nussinov R. Najafi S. Ngo S. T. Loquet A. Chiricotto M. Ganguly P. McCarty J. Li M. S. Hall C. Wang Y. Miller Y. Melchionna S. Habenstein B. Timr S. Chen J. Hnath B. Strodel B. Kayed R. Lesné S. Wei G. Sterpone F. Doig A. J. Derreumaux P. Amyloid oligomers: A joint experimental/computational perspective on Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Type II diabetes, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 2021;121:2545–2647. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

