Melatonin induces drought stress tolerance by regulating the physiological mechanisms, antioxidant enzymes, and leaf structural modifications in Rosa centifolia L
- PMID: 39811314
- PMCID: PMC11729657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41236
Melatonin induces drought stress tolerance by regulating the physiological mechanisms, antioxidant enzymes, and leaf structural modifications in Rosa centifolia L
Abstract
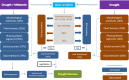
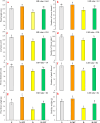
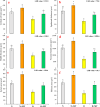
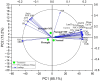
Melatonin is considered an effective bio-stimulant that is crucial in managing several abiotic stresses including drought. However, its potential mechanisms against drought stress in fragrant roses are not well understood. Here, we aim to investigate the role of melatonin on Rosa centifolia plants cultivated under drought stress (40 % field capacity) and normal irrigation (80 % field capacity). Plant growth traits, gaseous exchange, antioxidants, osmolytes, oxidative stress, and leaf anatomical attributes were measured. All pots were arranged with a completely randomized design with two-factor factorial setup. Foliar application of melatonin was carried out on the next day of drought treatment and was repeated weekly, while normal watering was regarded as control. Drought stress significantly enhanced oxidative stress markers and reduced growth parameters in water-deficit rose plants. However, melatonin spray (100 μM) produced increased plant height (16 %), flower yield (16 %), petal fresh and dry biomass (7 % and 38 %), total chlorophyll (48 %), contents of carotenoid (54 %), and gaseous exchange traits such as stomatal conductance (25 %), photosynthetic rate (91 %), and transpiration rate (3 %), in water-deficient plants. Likewise, the accretion of catalase, superoxide dismutase, soluble protein, proline, and glycine betaine contents was recorded by 22 %, 45 %, 58 %, 7 %, and 6 %, respectively, in drought-stressed plants, due to melatonin treatment. Increment of oxidative stress indicators i.e. malondialdehyde (-37 %) and hydrogen peroxide (-27 %) was diminished by melatonin triggered by drought stress. Furthermore, leaf cortex (51 %), vascular bundle area (76 %), palisade cell area (59 %), and lamina thickness (42 %) were remarkably increased with melatonin foliar sprays in water-deficit plants. The results of this study recommend that melatonin is a protective agent against drought stress and has potential application prospects in the rose-producing regions suffering from water deficiency. Future studies should focus on molecular responses of R. centifolia to drought stress to further develop stress alleviation strategies in floricultural crops.
Keywords: Enzyme activity; Photosynthesis; Proline; Sustainable floriculture; Water deficiency.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Ahsan M., et al. Morpho-physiological and enzymatic responses of zinnia (Zinnia elegans l.) to different metal hoarded wastewaters. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024;24:2910–2923. doi: 10.1007/s42729-024-01717-w. - DOI
-
- Zomorrodi N., et al. Potency of titanium dioxide nanoparticles, sodium hydrogen sulfide and salicylic acid in ameliorating the depressive effects of water deficit on periwinkle ornamental quality. Horticulturae. 2022;8:675. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae8080675. - DOI
-
- Toscano S., Romano D. Morphological, physiological, and biochemical responses of zinnia to drought stress. Horticulturae. 2021;7:362. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7100362. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

