Proteasome inhibition induces microtubule-dependent changes in nuclear morphology
- PMID: 39811669
- PMCID: PMC11729685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111550
Proteasome inhibition induces microtubule-dependent changes in nuclear morphology
Abstract
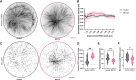
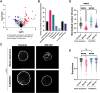
Cancers and neurodegenerative disorders are associated with both disrupted proteostasis and altered nuclear morphology. Determining if changes in nuclear morphology contribute to pathology requires an understanding of the underlying mechanisms, which are difficult to elucidate in cells where pleiotropic effects of altering proteostasis might indirectly influence nuclear morphology. To investigate direct effects, we studied nuclei assembled in Xenopus egg extract where potentially confounding effects of transcription, translation, cell cycle progression, and actin dynamics are absent. We report that proteasome inhibition causes acute microtubule-dependent changes in nuclear morphology and stability and altered microtubule dynamics and organization. Proteomic analysis of proteasome-inhibited extracts identified an increased abundance of microtubule nucleator TubGCP6, and TubGCP6 depletion partially rescued nuclear morphology. Key results were confirmed in HeLa cells. We propose that accumulation of TubGCP6 leads to altered microtubule dynamics proximal to the nucleus, producing forces that deform the nucleus and impact nuclear morphology and integrity.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cell biology; Functional aspects of cell biology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nuclear F-actin and Lamin A antagonistically modulate nuclear shape.J Cell Sci. 2022 Jul 1;135(13):jcs259692. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259692. Epub 2022 Jul 4. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 35665815 Free PMC article.
-
Altered nuclear dynamics in MDX myofibers.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Mar 1;122(3):470-481. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00857.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 27979987 Free PMC article.
-
Emerin induces nuclear breakage in Xenopus extract and early embryos.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Dec 15;29(26):3155-3167. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-05-0277. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30332321 Free PMC article.
-
The Cytoskeleton and Its Roles in Self-Organization Phenomena: Insights from Xenopus Egg Extracts.Cells. 2021 Aug 26;10(9):2197. doi: 10.3390/cells10092197. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule dynamics in Xenopus egg extracts.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Mar 15;44(6):435-45. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19990315)44:6<435::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-T. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10211677 Review.
Cited by
-
How the chromatin landscape influences nuclear morphology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 3;13:1634252. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1634252. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40677919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

