Infection control nurse: A scoping review
- PMID: 39811859
- PMCID: PMC11731345
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_217_24
Infection control nurse: A scoping review
Abstract
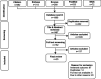
Infection control is a crucial aspect of healthcare delivery aimed at curtailing the spread of infections within healthcare settings. The role of infection control nurses (ICNs) is reported to have a significant contribution in limiting healthcare-associated infections. Scholarly investigations have explored various domains of ICNs. However, a lack of comprehensive coverage of existing studies in the area is observed. Therefore, the current review attempts to determine the scope of the literature published on ICNs. A search was conducted on PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, Embase, and Web of Science from January 2000 to December 2023 to retrieve research outputs on ICNs. The identified data underwent two screening stages to extract relevant articles based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The key outcomes were the factors that influenced the performance of ICNs and ICN programs. Out of 1869 articles, 25 were selected for the final review. The study summary identifies themes such as the roles and factors influencing ICNs and evaluating ICN programs. The review highlights a lack of high-quality evidence on ICN programs. Therefore, future studies should focus on implementing and evaluating these programs. Mapping and designing the structure, job responsibilities, and the role of ICNs demand attention from the research community.
Keywords: Infection control; infection control nurse; infection control practice; infection control program; scoping review.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Mitchell BG, Gardner A, Stone PW, Hall L, Pogorzelska-Maziarz M. Hospital staffing and health care-associated infections: A systematic review of the literature. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2018;44:613–22. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources