SKP1-CUL1-F-box: Key molecular targets affecting disease progression
- PMID: 39812503
- PMCID: PMC11734646
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202402816RR
SKP1-CUL1-F-box: Key molecular targets affecting disease progression
Abstract
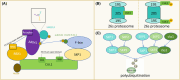
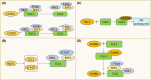
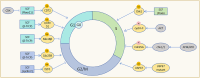
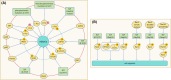
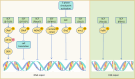
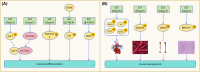
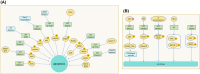
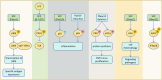
The correct synthesis and degradation of proteins are vital for numerous biological processes in the human body, with protein degradation primarily facilitated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. The SKP1-CUL1-F-box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase, a member of the Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL) family, plays a crucial role in mediating protein ubiquitination and subsequent 26S proteasome degradation during normal cellular metabolism. Notably, SCF is intricately linked to the pathogenesis of various diseases, including malignant tumors. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the functional characteristics of SCF complexes, encompassing their assembly, disassembly, and regulatory factors. Furthermore, we discuss the diverse effects of SCF on crucial cellular processes such as cell cycle progression, DNA replication, oxidative stress response, cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell differentiation, maintenance of stem cell characteristics, tissue development, circadian rhythm regulation, and immune response modulation. Additionally, we summarize the associations between SCF and the onset, progression, and prognosis of malignant tumors. By synthesizing current knowledge, this review aims to offer a novel perspective for a holistic and systematic understanding of SCF complexes and their multifaceted functions in cellular physiology and disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: CUL1; F‐box; SKP1; disease progression; molecular target.
© 2025 The Author(s). The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetically engineered mouse models for functional studies of SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligases.Cell Res. 2013 May;23(5):599-619. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.44. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23528706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of SKP1-CUL1-F-box-protein (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligases in skin cancer.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Mar 20;40(3):97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 10. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23522382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34 and ubiquitin ligase Skp1-cullin-F-box ligase (SCF) interact through multiple conformations.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 9;290(2):1106-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.615559. Epub 2014 Nov 25. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25425648 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SCF ubiquitin ligases by engineered ubiquitin variants that target the Cul1 binding site on the Skp1-F-box interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 29;113(13):3527-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519389113. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26976582 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neddylation and deneddylation of cullin1 in SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase by F-box protein and substrate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 1;103(31):11515-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603921103. Epub 2006 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16861300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of cullin family genes in rectal adenocarcinoma: expression, prognostic significance, and therapeutic implications.Am J Transl Res. 2025 May 15;17(5):3842-3861. doi: 10.62347/UNVS8140. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40535676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandra Dantu S, Nathubhai Kachariya N, Kumar A. Molecular dynamics simulations elucidate the mode of protein recognition by Skp1 and the F‐box domain in the SCF complex. Proteins. 2016;84(1):159‐171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

