Illuminating the impact of N-terminal acetylation: from protein to physiology
- PMID: 39814713
- PMCID: PMC11735805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55960-5
Illuminating the impact of N-terminal acetylation: from protein to physiology
Abstract
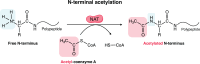
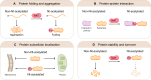
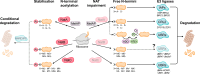
N-terminal acetylation is a highly abundant protein modification in eukaryotic cells. This modification is catalysed by N-terminal acetyltransferases acting co- or post-translationally. Here, we review the eukaryotic N-terminal acetylation machinery: the enzymes involved and their substrate specificities. We also provide an overview of the impact of N-terminal acetylation, including its effects on protein folding, subcellular targeting, protein complex formation, and protein turnover. In particular, there may be competition between N-terminal acetyltransferases and other enzymes in defining protein fate. At the organismal level, N-terminal acetylation is highly influential, and its impairment was recently linked to cardiac dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 324195/Norges Forskningsråd (Research Council of Norway)
- 325142/Norges Forskningsråd (Research Council of Norway)
- 772039/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

