Cause and consequences of Common Snook (Centropomus undecimalis) space use specialization in a subtropical riverscape
- PMID: 39814810
- PMCID: PMC11736134
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-82158-4
Cause and consequences of Common Snook (Centropomus undecimalis) space use specialization in a subtropical riverscape
Abstract
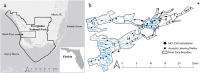
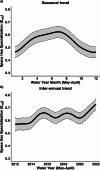
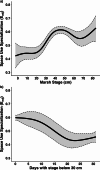
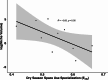
Variability in space use among conspecifics can emerge from foraging strategies that track available resources, especially in riverscapes that promote high synchrony between prey pulses and consumers. Projected changes in riverscape hydrological regimes due to water management and climate change accentuate the need to understand the natural variability in animal space use and its implications for population dynamics and ecosystem function. Here, we used long-term tracking of Common Snook (Centropomus undecimalis) movement and trophic dynamics in the Shark River, Everglades National Park from 2012 to 2023 to test how specialization in the space use of individuals (i.e., Eadj) changes seasonally, how it is influenced by yearly hydrological conditions, and its relationship to the between individual trophic niche. Snook exhibited seasonal variability in space use, with maximum individual specialization (high dissimilarity) in the wet season. The degree of individual specialization increased over the years in association with greater marsh flooding duration, which produced important subsidies. Also, there were threshold responses of individual space use specialization as a function of floodplain conditions. Greater specialization in space use results in a decrease in snook trophic niche size. These results show how hydrological regimes in riverscapes influence individual specialization of resource use (both space and prey), providing insight into how forecasted hydroclimatic scenarios may shape habitat selection processes and the trophic dynamics of mobile consumers.
Keywords: Acoustic telemetry; Everglades; Habitat use similarity; Movement ecology; Trophic niche.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The Florida International University Institution Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC-18-002-CR01) approved the project’s sampling and animal handling protocol. Project activities were conducted under the Everglades National Park research permit EVER-2022-SCI-0056. This study is reported following ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- McPeek, M. A. & Holt, R. D. The evolution of Dispersal in spatially and temporally varying environments. Am. Nat.140, 1010–1027 (1992).
-
- Mueller, T. & Fagan, W. F. Search and navigation in dynamic environments – from individual behaviors to population distributions. Oikos117, 654–664 (2008).
-
- Abrahms, B. et al. Emerging perspectives on resource tracking and animal movement ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol.36, 308–320 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

