Cationic peptides cause memory loss through endophilin-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 39814881
- PMCID: PMC12413077
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08413-w
Cationic peptides cause memory loss through endophilin-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
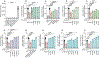
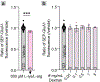
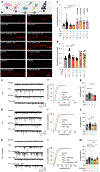
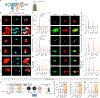
The zeta inhibitory peptide (ZIP) interferes with memory maintenance and long-term potentiation (LTP)1 when administered to mice. However, mice lacking its putative target, protein kinase PKMζ, exhibit normal learning and memory as well as LTP2,3, making the mechanism of ZIP unclear. Here we show that ZIP disrupts LTP by removing surface AMPA receptors through its cationic charge alone. This effect requires endophilin-A2-mediated endocytosis and is fully blocked by drugs suppressing macropinocytosis. ZIP and other cationic peptides remove newly inserted AMPA receptor nanoclusters at potentiated synapses, providing a mechanism by which these peptides erase memories without altering basal synaptic function. When delivered in vivo, cationic peptides can modulate memories on local and brain-wide scales, and these mechanisms can be leveraged to prevent memory loss in a model of traumatic brain injury. Our findings uncover a previously unknown synaptic mechanism by which memories are maintained or lost.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
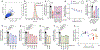








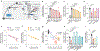


Update of
-
Cationic peptides erase memories by removing synaptic AMPA receptors through endophilin-mediated endocytosis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 21:rs.3.rs-3559525. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3559525/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nature. 2025 Feb;638(8050):479-489. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08413-w. PMID: 38045269 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Pastalkova E et al. Storage of spatial information of LTP by the maintenance mechanism. Science 313, 1141–1144 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 DA041445/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 GM126136/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 GM150017/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116901/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH129620/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS130044/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS132447/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AG067666/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS096012/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DA056215/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA056599/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA054374/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

