DeepDrug as an expert guided and AI driven drug repurposing methodology for selecting the lead combination of drugs for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39814937
- PMCID: PMC11735786
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85947-7
DeepDrug as an expert guided and AI driven drug repurposing methodology for selecting the lead combination of drugs for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
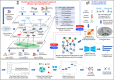
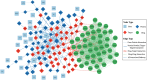
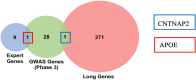
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) significantly aggravates human dignity and quality of life. While newly approved amyloid immunotherapy has been reported, effective AD drugs remain to be identified. Here, we propose a novel AI-driven drug-repurposing method, DeepDrug, to identify a lead combination of approved drugs to treat AD patients. DeepDrug advances drug-repurposing methodology in four aspects. Firstly, it incorporates expert knowledge to extend candidate targets to include long genes, immunological and aging pathways, and somatic mutation markers that are associated with AD. Secondly, it incorporates a signed directed heterogeneous biomedical graph encompassing a rich set of nodes and edges, and node/edge weighting to capture crucial pathways associated with AD. Thirdly, it encodes the weighted biomedical graph through a Graph Neural Network into a new embedding space to capture the granular relationships across different nodes. Fourthly, it systematically selects the high-order drug combinations via diminishing return-based thresholds. A five-drug lead combination, consisting of Tofacitinib, Niraparib, Baricitinib, Empagliflozin, and Doxercalciferol, has been selected from the top drug candidates based on DeepDrug scores to achieve the maximum synergistic effect. These five drugs target neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and glucose metabolism, which are all related to AD pathology. DeepDrug offers a novel AI-and-big-data, expert-guided mechanism for new drug combination discovery and drug-repurposing across AD and other neuro-degenerative diseases, with immediate clinical applications.
Keywords: Aging pathways; Alzheimer’s Disease; DeepDrug; Directed biomedical graph; Expert-led AI drug-repurposing; Graph neural network; Immunological; Inflammation; Lead combination of AD drugs; Long genes; Neuro-degenerative; Pathway convergence; Somatic and germline mutations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: This work, including contribution of six of the co-authors (VL, YH, TK, JD, IG, and JL), has been submitted for patent protection (University of Hong Kong and Tel Aviv University). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Drug repurposing using artificial intelligence, molecular docking, and hybrid approaches: A comprehensive review in general diseases vs Alzheimer's disease.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025 Apr;261:108604. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2025.108604. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39826482 Review.
-
Medical genetics-based drug repurposing for Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2015 Jan;110:26-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 22. Brain Res Bull. 2015. PMID: 25446738 Review.
-
Mining on Alzheimer's diseases related knowledge graph to identity potential AD-related semantic triples for drug repurposing.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 30;23(Suppl 6):407. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04934-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36180861 Free PMC article.
-
DRTerHGAT: A drug repurposing method based on the ternary heterogeneous graph attention network.J Mol Graph Model. 2024 Jul;130:108783. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2024.108783. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Mol Graph Model. 2024. PMID: 38677034
-
Repurposed Drugs as Potential Therapeutic Candidates for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Drug Metab. 2017;18(9):842-852. doi: 10.2174/1389200218666170607101622. Curr Drug Metab. 2017. PMID: 28595531 Review.
Cited by
-
Target identification of natural products in cancer with chemical proteomics and artificial intelligence approaches.Cancer Biol Med. 2025 Jul 9;22(6):549-97. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2025.0145. Cancer Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40631551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Doxycycline: An essential tool for Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Jul;188:118159. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118159. Epub 2025 May 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40367557 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prince, M. J. et al. World Alzheimer Report 2015-The Global Impact of Dementia: An analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. (2015).
-
- Prince, M. et al. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement.9, 63-75.e62 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Wu, Y.-T. et al. The changing prevalence and incidence of dementia over time—Current evidence. Nat. Rev. Neurol.13, 327–339 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

