ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters: structures and roles in bacterial pathogenesis
- PMID: 39815611
- PMCID: PMC11735909
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2300641
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters: structures and roles in bacterial pathogenesis
Abstract
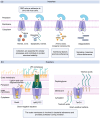
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette (ABC) transporter systems are divided into importers and exporters that facilitate the movement of diverse substrate molecules across the lipid bilayer, against the concentration gradient. These transporters comprise two highly conserved nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) and two transmembrane domains (TMDs). Unlike ABC exporters, prokaryotic ABC importers require an additional substrate-binding protein (SBP) as a recognition site for specific substrate translocation. The discovery of a large number of ABC systems in bacterial pathogens revealed that these transporters are crucial for the establishment of bacterial infections. The existing literature has highlighted the roles of ABC transporters in bacterial growth, pathogenesis, and virulence. These roles include importing essential nutrients required for a variety of cellular processes and exporting outer membrane-associated virulence factors and antimicrobial substances. This review outlines the general structures and classification of ABC systems to provide a comprehensive view of the activities and roles of ABC transporters associated with bacterial virulence and pathogenesis during infection.
腺苷三磷酸结合盒转运蛋白(ATP-binding cassette transporter proteins,ABC转运蛋白)具有向外和向内两种转运方式,能通过克服浓度梯度协助多种底物分子在磷脂双分子层中运输。这些转运蛋白具有两个高度保守的核苷酸结合区域(NBDs)和两个跨膜结构域(TMDs)。与ABC向外转运蛋白不同,原核生物的ABC向内转运蛋白还需额外的底物结合蛋白(SBP)作为特定底物转运的识别位点。大量研究发现在细菌致病体中存在许多ABC转运蛋白,提示这些转运蛋白对细菌感染的建立至关重要。现有研究证实,ABC转运蛋白在细菌生长、致病和毒力方面发挥作用,包括导入细胞活动所需的必要营养物质,以及输出与外膜相关的毒力因子和抗微生物物质等。本文对ABC转运蛋白的经典结构和最新分类进行综述,以便全面了解与细菌毒力和致病性相关的ABC转运蛋白在细菌感染期间的活动与作用。.
腺苷三磷酸结合盒转运蛋白(ATP-binding cassette transporter proteins,ABC转运蛋白)具有向外和向内两种转运方式,能通过克服浓度梯度协助多种底物分子在磷脂双分子层中运输。这些转运蛋白具有两个高度保守的核苷酸结合区域(NBDs)和两个跨膜结构域(TMDs)。与ABC向外转运蛋白不同,原核生物的ABC向内转运蛋白还需额外的底物结合蛋白(SBP)作为特定底物转运的识别位点。大量研究发现在细菌致病体中存在许多ABC转运蛋白,提示这些转运蛋白对细菌感染的建立至关重要。现有研究证实,ABC转运蛋白在细菌生长、致病和毒力方面发挥作用,包括导入细胞活动所需的必要营养物质,以及输出与外膜相关的毒力因子和抗微生物物质等。本文对ABC转运蛋白的经典结构和最新分类进行综述,以便全面了解与细菌毒力和致病性相关的ABC转运蛋白在细菌感染期间的活动与作用。
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter; Bacterial pathogenesis; Virulence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective substrate uptake: The role of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) importers in pathogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Apr;1860(4):868-877. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 28847505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of bacterial ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in pathogenesis and virulence: Therapeutic and vaccine potential.Microb Pathog. 2022 Oct;171:105734. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105734. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36007845 Review.
-
Structurally diverse C-terminal accessory domains in type I ABC importers reveal distinct regulatory mechanisms.Structure. 2025 May 1;33(5):843-857. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2025.02.014. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Structure. 2025. PMID: 40132581 Review.
-
Conformational coupling of the nucleotide-binding and the transmembrane domains in ABC transporters.Biophys J. 2011 Aug 3;101(3):680-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.031. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21806936 Free PMC article.
-
One Intact Transmembrane Substrate Binding Site Is Sufficient for the Function of the Homodimeric Type I ATP-Binding Cassette Importer for Positively Charged Amino Acids Art(MP)2 of Geobacillus stearothermophilus.J Bacteriol. 2018 May 24;200(12):e00092-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00092-18. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29581409 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative genomic analysis of emerging non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) causing emerging septic arthritis in Atlanta.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 21;13:e19081. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19081. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40130174 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

