A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors and Their Impact on the Management of Heart Failure
- PMID: 39816302
- PMCID: PMC11734706
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75802
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors and Their Impact on the Management of Heart Failure
Abstract
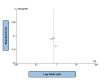
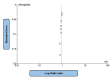
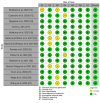
Heart failure (HF) is a life-threatening condition with severe incapacitating consequences. Many body organs and systems may be affected, which may also hinder the quality of life and finances at the individual and societal levels. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have also emerged as potentially useful drugs in the HF domain and other medical fields, in addition to their glucose-lowering effect. This systematic review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, and the authors searched Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus websites for SGLT2i and SGLT2i-related terms and their impact on HF events, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), renal composite outcomes, and improvement in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) scores, involving human adult populations. Two reviewers conducted the literature search, and disagreements were resolved through mutual consensus and input from a third reviewer. A literature search was conducted from 1st February to 20th February 2024. We included studies published after 2018 to focus only on the latest advancements. Randomized controlled trials, observational studies, or systematic reviews of these studies were included in our study. Of the 44 initial articles identified, only 14 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The outcomes revealed the superiority of SGLT2i therapeutics over placebo in all four domains mentioned above. A total of 234,509 patients from 11 papers with moderate heterogeneity (P = 0.07; I2 = 42%) evaluating the effect of SGLT2i in comparison to placebo on HF events were considered; of these, 128,477 patients received the intervention drug, and 106,032 individuals were assigned to the control group. The absolute numbers of HF events were 6845 and 8877, respectively. The study showed an overall benefit of SGLT2i in patients with heart failure due to their ability to major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in comparison to placebo (OR: 0.92; 95% CI: 0.89-0.96; P < 0.00001). This systematic review confirmed previous findings related to the use of SGLT2i as adjunctive therapy for HF and amelioration of KCCQ scores and as a protective agent against MACE and renal impairment progression.
Keywords: heart failure hospitalization; heart failure management programmes; heart failure prognosis; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; major adverse cardiovascular events (mace); preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses(prisma); remote monitoring of heart failure; sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (sglt2) inhibitors; systolic heart failure.
Copyright © 2024, Lemos Ferreira et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
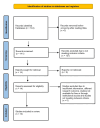







Similar articles
-
Effects of different sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in heart failure with reduced or preserved ejection fraction: a network meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 May 23;11:1379765. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1379765. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38845687 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiac function and health status in chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jan 3;23(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02042-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38172861 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors, Functional Capacity, and Quality of Life in Patients With Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Apr 1;7(4):e245135. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5135. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38573633 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on cardiovascular and renal outcomes according to renal function: a dose-response meta-analysis involving 10 randomized clinical trials and 71 553 individuals.Eur J Endocrinol. 2023 Jul 20;189(1):S17-S25. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad078. Eur J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37474112
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Am J Med. 2020 Nov;133(11):e625-e630. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 May 7. Am J Med. 2020. PMID: 32389659
References
-
- The impact of case management on reducing readmission for patients diagnosed with heart failure and diabetes. McCants KM, Reid KB, Williams I, Miller DE, Rubin R, Dutton S. Prof Case Manage. 2019;24:177–193. - PubMed
-
- 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. Eur Heart J. 2023;1:3627–3639. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
