Optimization of green tea extract, rosemary extract, and rice bran in multifunctional bread: A concept for reduction of acrylamide and phytic acid
- PMID: 39816510
- PMCID: PMC11732667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41182
Optimization of green tea extract, rosemary extract, and rice bran in multifunctional bread: A concept for reduction of acrylamide and phytic acid
Abstract
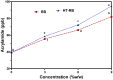
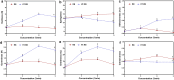
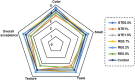
This research aimed to produce a multifunctional bread by adding hydrothermally processed rice bran (RB), green tea extract (GTE), and rosemary extract (RE). In the first step, hydrothermal processing was used to reduce the amount of phytic acid in RB, which decreased by 55 %. Based on the acrylamide amount, texture profile analysis, and color parameters, 3 % RB was selected as the optimum concentration in the bread formulation. The acrylamide amount in the RB-fortified bread showed a significant (p < 0.05) reduction trend with the addition of GTE and RE. So the lowest amount of acrylamide concentration was reported in the sample containing 1.5 % GTE (17.18 ppb). The addition of GTE and RE significantly (p < 0.05) decreased the hardness value of bread samples. However, the cohesiveness, springiness, and adhesiveness parameters of bread samples were significantly (p < 0.05) increased by the addition of GTE and RE. In addition, the fortified breads with 0.1 % RE and 1.5 % GTE exhibited the lowest and highest ΔE values, respectively. The addition of GTE and RE caused no adverse effect on the sensory properties of the RB-fortified bread. In conclusion, the combination of RB, GTE, and/or RE is an effective strategy for providing health benefits as well as reducing acrylamide formation in this food.
Keywords: Acrylamide; Functional bread; Hydrothermal process; Millard; Phytic acid.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of concentrated and dephytinized wheat bran and rice bran addition on bread properties.J Texture Stud. 2018 Feb;49(1):84-93. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12286. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Texture Stud. 2018. PMID: 28742221
-
Effect of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) extracted from green tea in reducing the formation of acrylamide during the bread baking process.Food Chem. 2018 Mar 1;242:162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.050. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29037673
-
Quality attributes of bread fortified with staghorn sumac extract.J Texture Stud. 2018 Feb;49(1):129-134. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12283. Epub 2017 Aug 6. J Texture Stud. 2018. PMID: 28710877
-
Study on reduction of acrylamide in fried bread sticks by addition of antioxidant of bamboo leaves and extract of green tea.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16 Suppl 1:131-6. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17392091
-
Effects of Hot-Water Extract from Vine Tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) on Acrylamide Formation, Quality and Consumer Acceptability of Bread.Foods. 2020 Mar 23;9(3):373. doi: 10.3390/foods9030373. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32210179 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring Formation and Control of Hazards in Thermal Processing for Food Safety.Foods. 2025 Jun 21;14(13):2168. doi: 10.3390/foods14132168. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40646920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ebrahimi M., Ali Noori S.M., Sadeghi A., emir Coban O., Zanganeh J., Ghodsmofidi S.M., Malvandi Z., Raeisi M. Application of cereal-bran sourdoughs to enhance technological functionality of white wheat bread supplemented with pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo) puree. LWT. 2022;158 doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113079. - DOI
-
- Jakubczyk A., Świeca M., Gawlik-Dziki U., Dziki D. Nutritional potential and inhibitory activity of bread fortified with green coffee beans against enzymes involved in metabolic syndrome pathogenesis. LWT. 2018;95:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.04.071. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

