Outcomes of liposuction techniques for management of lipedema: a case series and narrative review
- PMID: 39817245
- PMCID: PMC11729798
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-24-165
Outcomes of liposuction techniques for management of lipedema: a case series and narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Lipedema is a commonly underdiagnosed chronic condition. This study aimed to evaluate liposuction techniques for lipedema by conducting a systematic review and presenting our experience. A case series study and a comprehensive review were conducted.
Methods: We assessed surgical outcomes among patients with lipedema who underwent liposuction. Descriptive and inferential statistics were implemented. In our case series, we used tumescent liposuction, vibration amplification of sound energy at resonance (VASER) liposuction, and waterjet-assisted liposuction (WAL). We also performed a literature review of current concepts and state-of-the-art treatment for lipedema.
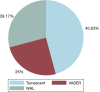
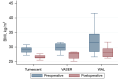
Key content and findings: Twenty-four female patients were included in this study with a median age of 37 years [interquartile range (IQR), 10 years]. A statistically significant difference between preoperative (29.65 kg/m2) and postoperative body mass index (BMI) (26.95 kg/m2; P<0.05) of patients was evidenced. The amount of total fat removal between surgical techniques was statistically different (P<0.001). A statistically significant difference in the amount of total fat removal between surgical techniques was found (P=0.0015). Post-hoc analysis with Dunn's test evidenced a significant difference only between tumescent suction-assisted lipectomy and WAL (P<0.001). Nineteen studies were included in this review. Low complication rates, improvement in patient-reported outcomes, and reduction in conservative therapy requirements were found when evaluating multiple studies in this review.
Conclusions: Liposuction has been shown to be a safe and effective alternative in patients with lipedema. It positively impacts clinical and patient-reported outcomes.
Keywords: Lipedema; case series; lipectomies; liposuction; suction.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-24-165/coif). O.J.M. serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Annals of Translational Medicine from July 2024 to June 2026. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
