Vδ2 T-cells response in people with Mpox infection: a three-month longitudinal assessment
- PMID: 39817429
- PMCID: PMC11792154
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2455585
Vδ2 T-cells response in people with Mpox infection: a three-month longitudinal assessment
Abstract
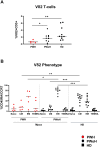
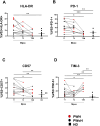
The first evidence that Orthopoxvirus induced the expansion in vivo and the recall of effector innate Vδ2 T-cells was described in a macaque model. Although, an engagement of αβ T-cells specific response in patients infected with human monkeypox (Mpox) was demonstrated, little is known about the role of γδ T-cells during Mpox infection. IFN-γ-producing γδ T-cells in the resistance to poxviruses may a key role in inducing a protective type 1 memory immunity. We analyzed the kinetics of Vδ2 T-cell response from the acute phase up to three months after Mpox infection. Fourteen MSM subjects (5 PWH, 35.7%) were enrolled in a longitudinal study from May to July 2022. Blood samples were collected in the early phase of infection (T1, T2) and at 3 months (T3M) post-symptom onset. Vδ2 T-cell profiles (CD45RA/CCR7), activation/exhaustion markers (CD38/HLA-DR/CD57/PD-1/TIM-3), cytokine production (IFN-γ/TNF-α) and CD107a expression were assessed by multiparametric flow cytometry. Ten healthy donors (HD) were used as a control group. At T1, Vδ2 T-cell frequency of patients decreased, and effector memory Vδ2 T-cells increased with respect to HD. Activation/exhaustion markers were higher than HD. Vδ2 functionality decreased at T1 related to HD, and it was associated with CD38 and HLA-DR higher expression as well as TIM-3. Vδ2 T-cells restored their profile at T3M. The presence of effector/activated Vδ2 T-cells in the early stages of Mpox infection and their capability to activate quickly, producing pro-inflammatory cytokines, may be useful to enhance the early adaptive response to human Mpox, maintaining a protective memory/effector T-cell response.
Keywords: Innate immunity; Mpox; Vδ2 T-cells; emerging viruses; exhaustion.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization ; [cited 2024 May 18]. Available from: https://www.who.int/europe/news/item/23-07-2022-who-director-general-dec...
-
- [cited 2024 Jun 03]. Available from: https://monkeypoxreport.ecdc.europa.eu/
-
- Zucker J. CROI 2023: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of mpox; [2023 Apr 19]. Available from: https://www.iasusa.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/30-3-zucker-v1.pdf - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
