Opposing roles of p38α-mediated phosphorylation and PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation in driving TDP-43 proteinopathy
- PMID: 39817908
- PMCID: PMC11831926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115205
Opposing roles of p38α-mediated phosphorylation and PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation in driving TDP-43 proteinopathy
Erratum in
-
Opposing roles of p38α-mediated phosphorylation and PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation in driving TDP-43 proteinopathy.Cell Rep. 2025 Mar 25;44(3):115386. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115386. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 39977265 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
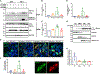
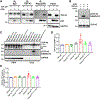
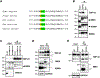
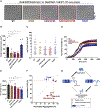
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder typically characterized by insoluble inclusions of hyperphosphorylated TDP-43. The mechanisms underlying toxic TDP-43 accumulation are not understood. Persistent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is implicated in ALS. However, it is unclear how p38 MAPK affects TDP-43 proteinopathy. Here, we show that p38α MAPK inhibition reduces pathological TDP-43 phosphorylation, aggregation, cytoplasmic mislocalization, and neurotoxicity. Remarkably, p38α MAPK inhibition mitigates aberrant TDP-43 phenotypes in diverse ALS patient-derived motor neurons. p38α MAPK phosphorylates TDP-43 at pathological S409/S410 and S292, which reduces TDP-43 liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) but allows pathological TDP-43 aggregation. Moreover, we establish that PRMT1 methylates TDP-43 at R293. Importantly, S292 phosphorylation reduces R293 methylation, and R293 methylation reduces S409/S410 phosphorylation. Notably, R293 methylation permits TDP-43 LLPS and reduces pathological TDP-43 aggregation. Thus, strategies to reduce p38α-mediated TDP-43 phosphorylation and promote PRMT1-mediated R293 methylation could have therapeutic utility for ALS and related TDP-43 proteinopathies.
Keywords: ALS; CP: Molecular biology; CP: Neuroscience; PRMT1; TDP-43; arginine methylation; p38α; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.J.W., D.G.B., and N.J.B. were full-time employees and shareholders of AstraZeneca at the time these studies were conducted. S.J.M. is a consultant for SAGE Therapeutics and AstraZeneca, relationships that are regulated by Tufts University.
Figures

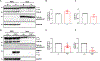
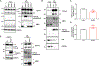
References
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, and Oda T (2006). TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

