Clustering and drivers of symptoms observed at week six after antidepressant treatment in depressed outpatients
- PMID: 39819366
- PMCID: PMC11795446
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.1801
Clustering and drivers of symptoms observed at week six after antidepressant treatment in depressed outpatients
Abstract
Background: Depressive symptoms remaining after antidepressant treatment increase the risk of relapse and recurrence. We aimed to analyze the distribution and main drivers of remaining symptoms in patients with a major depressive episode.
Methods: Two independent samples of 8,229 and 5,926 patients from two large naturalistic studies were retrospectively analyzed. DSM-IV criteria for major depressive episodes were assessed during two face-to-face visits with clinicians: before the prescription of a new antidepressant, and after 6 weeks of treatment. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to assess baseline severity of anxiety and depression.
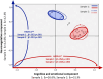
Results: In both samples, two clusters of remaining symptoms were observed. The first cluster encompassed symptoms related to a negative emotional and cognitive bias and was specifically driven by the baseline severity of depression. The second cluster encompassed neurovegetative symptoms and was specifically driven by the baseline severity of anxiety.
Conclusions: The baseline anxiety-depressive balance of patients could be considered to adapt the treatment, focusing on emotional and cognitive symptoms with patients with high baseline severity of depression, and neurovegetative symptoms with patients with high baseline anxiety severity.
Keywords: anxiety; cognitive; depression; emotional; residual symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
PG received during the last 5 years fees for presentations at congresses or participation in scientific boards from Angelini, Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka, and Viatris. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou J, Zhou J, Feng Z, Feng L, Xiao L, Chen X, et al. Identifying the core residual symptom in patients with major depressive disorder using network analysis and illustrating its association with prognosis: a study based on the national cohorts in China. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2024;87:68–76. 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2024.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

