Modified lung ultrasound score for improved monitoring of pARDS on ECMO, a case report
- PMID: 39819488
- PMCID: PMC11736947
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-05308-7
Modified lung ultrasound score for improved monitoring of pARDS on ECMO, a case report
Abstract
Background: Lung ultrasound scoring is a validated tool for assessing lung pathology. However, existing scoring systems typically overlook the size of consolidations, limiting their accuracy in certain clinical scenarios.
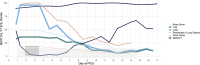
Case presentation: We describe the first application of adding the maximum consolidation depth in centimeters (cm) to the conventional score. This modification (LUS+) was used in an eight-month-old patient with severe respiratory failure undergoing extracorporeal life support (ECLS). Spearman's correlation analysis revealed a similar correlation in LUS+ compared to conventional lung ultrasound score. Importantly, LUS + showed improvement following cessation of lung rest on day 5, preceding the changes observed in conventional lung ultrasound scores and tidal volume measurements on day 9.
Conclusions: The integration of consolidation depth, quantified in centimeters, represents a valuable refinement of the conventional lung ultrasound score, enhancing its utility in monitoring pediatric acute respiratory distress patients undergoing ECLS.
Keywords: Case Report; Child; Extracorporeal Life Support; Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation; Infant; Lung; Lung Ultrasound Score; Pediatric Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome; Pediatric Critical Care; Prospective Studies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: As this is an observational case report and no therapeutic interventions were undertaken, ethical approval was waived following the informed consent. Informed consent for participation and publication was obtained from the legal guardians. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Küng E, Schwaberger B, Pramhofer N, Klemme M, Schneider M, Habrina L et al. Proposed Standard for Neonatologist Performed Lung Ultrasound [Internet]. Zenodo; 2024 Jun [cited 2024 Aug 26]. 10.5281/zenodo.3968810
-
- Via G, Storti E, Gulati G, Neri L, Mojoli F, Braschi A. Lung ultrasound in the ICU: from diagnostic instrument to respiratory monitoring tool. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012;78(11):1282–96. - PubMed
-
- Brat R, Yousef N, Klifa R, Reynaud S, De Shankar Aguilera S. Lung Ultrasonography score to evaluate oxygenation and surfactant need in neonates treated with continuous positive Airway pressure. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(8):e151797. - PubMed
-
- Di Nardo M, Lorusso R, Guner Y, Schomberg J, De Luca D. Feasibility of Lung Ultrasound to Monitor Aeration in Children supported with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. ASAIO J. 2021;67(6):e104–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

