Stigma in substance-based and behavioural addictions: A systematic review
- PMID: 39819679
- PMCID: PMC11974440
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.2024.00072
Stigma in substance-based and behavioural addictions: A systematic review
Abstract
Background and aims: The study of stigma contributes greatly to our understanding of individuals' experiences of mental disorders. Addictive disorders are often associated with public misconceptions of the disorder, which can contribute to shame, discrimination, and reticence to seek help. This review aimed to: (1) evaluate the nature, frequency, and prevalence of addiction stigma; (2) identify the correlates of addiction stigma; and (3) examine the psychometric qualities of addiction stigma measures.
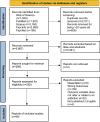
Methods: A search of Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, PsycINFO, and PsycNet, had 5,515 results which were screened for eligibility using Covidence. Eligible papers were quantitative, peer-reviewed studies, which reported an outcome variable of stigma related to an addiction.
Results: A total of 99 studies were included in the review, including 70 studies of substance-based addictions, 19 studies of behavioral addictions, and 10 studies which examined both. Thirteen of the 20 studies examining the impact of familiarity with addiction reported that greater familiarity was associated with lower public stigma. Studies comparing substance and behavioral addictions (n = 5) typically reported greater public stigma towards vignettes depicting substance-based addictions than for behavioral addictions. Between 22% and 40% of individuals with an addictive disorder identified stigma as a significant barrier to seeking help; however, the relative importance of stigma among other barriers was unclear.
Discussion and conclusions: Evidence for countermeasures to prevent and/or reduce stigma is currently limited. Further research on the nature and prevalence of addiction stigma is needed to inform the development of effective clinical and public health countermeasures.
Keywords: addiction; frequency; gambling; gaming; measurement; prejudice; stigma; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mass media interventions for reducing mental health-related stigma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 23;2013(7):CD009453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009453.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23881731 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Factors that influence participation in physical activity for people with bipolar disorder: a synthesis of qualitative evidence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 4;6(6):CD013557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013557.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38837220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychological therapies for post-traumatic stress disorder and comorbid substance use disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 4;4(4):CD010204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27040448 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Ahorsu, D. K., Lin, C. Y., Imani, V., Griffiths, M. D., Su, J. A., Latner, J. D., … Pakpour, A. H. (2020). A prospective study on the link between weight‐related self‐stigma and binge eating: Role of food addiction and psychological distress. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 53(3), 442–450. 10.1002/eat.23219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical