Impact of dumpsite compost on heavy metal accumulation in some cultivated plants
- PMID: 39819793
- PMCID: PMC11740349
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-025-07083-9
Impact of dumpsite compost on heavy metal accumulation in some cultivated plants
Abstract
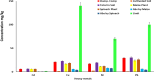
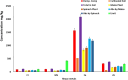
The study examines the concentrations of heavy metals in agricultural soil, compost from landfills, maize plants, and spinach crops. The results show that compost from landfills had levels exceeding EU requirements for Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn. However, agricultural soil contained trace amounts of heavy metals. The order of metal absorption by plants was Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr > Zn > Fe > Mn. This highlights potential health risks associated with consuming crops grown in compost or soil tainted with heavy metals.
Keywords: Dumpsite compost; Heavy metals; Human and animal health; Maize plant; Spinach plant.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health risk assessment of trace metals from spinach grown on compost-amended soil.Int J Phytoremediation. 2018;20(13):1330-1336. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2018.1488816. Int J Phytoremediation. 2018. PMID: 30666891
-
Accumulation, fractionation and health risk assessment of fluoride and heavy metals in soil-crop systems in northwest China.Sci Total Environ. 2019 May 1;663:307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.257. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30711597
-
Heavy metal distribution and uptake by maize in a mudflat soil amended by vermicompost derived from sewage sludge.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Oct;26(29):30154-30166. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06184-w. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31422536
-
A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge.Environ Int. 2009 Jan;35(1):142-56. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 8. Environ Int. 2009. PMID: 18691760 Review.
-
Bioaccumulation Factor of Selected Heavy Metals in Zea mays.J Health Pollut. 2019 Dec 6;9(24):191207. doi: 10.5696/2156-9614-9.24.191207. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Health Pollut. 2019. PMID: 31893168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Khatib IA, Kontogianni S, Abu Nabaa H, Alshami N. Sustainable waste management: waste-to-energy incineration plants as an alternative to landfill. J Environ Manag. 2015;156:102–13.
-
- Adewumi JR, Oladunjoye MA, Ogunjimi DA. Assessment of groundwater quality in a municipal solid waste dumpsite in Abeokuta, southwestern Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess. 2019;191(10):629. - PubMed
-
- Ojuri OO, Adegbite KA, Alagbe SA, Onibokun EA. Social and economic challenges of municipal solid waste management in Nigeria. 2018.
-
- Ajibade FO, Adewumi JR, Oyediran GO. Microbial degradation of textile dye effluent using indigenous bacteria isolated from dumpsite soil in Ogbomoso, Nigeria. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26(15):15359–70.
-
- Kanmani S, Gandhimathi R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil due to leachate migration from an open dumping site. Appl Water Sci. 2013;3:193–205. 10.1007/s13201-012-0072-z.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources