Effect of metformin on the clinical outcomes of stroke in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39819905
- PMCID: PMC11751969
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-092214
Effect of metformin on the clinical outcomes of stroke in patients with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Stroke is a major cause of death and disability globally, especially among diabetic patients. In this study, we aim to scrutinise the effects of metformin on the clinical outcomes of stroke in diabetic patients.
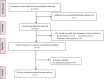
Design: This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines.
Data sources: PubMed, Embase and Web of Science databases were searched between their inception and 5 December 2023.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: Studies investigating the effect of metformin on the clinical outcomes of stroke in patients with diabetes were included.
Data extraction and synthesis: The effect of metformin on the clinical outcomes of stroke in patients with diabetes was identified using combined ORs and 95% CIs.
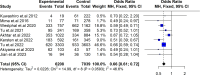
Results: A total of 11 studies involving 18 525 participants were included in this review. Pooled analysis has demonstrated that prestroke metformin use could reduce the probability of poor course after stroke by 34% in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients (OR=0.66, 95% CI: 0.61 to 0.72) and reduce the probability of death by 43% (OR=0.57, 95% CI: 0.51 to 0.64).
Conclusions: Prestroke metformin use is beneficial for the improvement of clinical outcomes in patients who had a stroke with DM, although the potential bias should be carefully considered.
Prospero registration number: CRD42024496056.
Keywords: Meta-Analysis; Prognosis; Stroke.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Metformin in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies.Clin Neuropharmacol. 2025 Mar-Apr 01;48(2):51-59. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0000000000000625. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40072880
-
The impact of pre-stroke metformin use on clinical outcomes after acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Jun;33(6):107716. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107716. Epub 2024 Apr 9. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38604350
-
Effects of continuous use of metformin on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes after acute myocardial infarction: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 16;100(15):e25353. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025353. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33847633 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular safety and efficacy of metformin-SGLT2i versus metformin-sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 8;11(1):137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80603-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33420333 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Metformin on the Severity and Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016 Feb;25(2):436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.10.016. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 26725260
Cited by
-
Repurposing Antidiabetic Drugs for Cerebrovascular Diseases: Causal Evidence from Drug Target Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Sep;62(9):11596-11610. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04987-2. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40301247
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical