Phase 1 study of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy harboring a fully human scFv in CAR-naïve adult patients with B-ALL
- PMID: 39820359
- PMCID: PMC12008683
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024015314
Phase 1 study of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy harboring a fully human scFv in CAR-naïve adult patients with B-ALL
Abstract
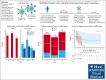
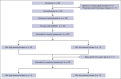
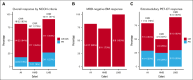
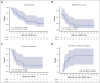
CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor-engineered (CAR) T-cell therapy elicits high response rates but fails to induce durable responses in most adults with relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). In a previous clinical trial, we observed anti-CAR immune responses associated with impaired in vivo CAR T-cell expansion after second infusions. Because these CD8+ T-cell responses were predominantly directed at peptides derived from the murine single-chain variable fragment (scFv) in the CAR, we conducted a clinical trial investigating the safety and efficacy of CD19 CAR T-cells engineered with a CAR incorporating a fully human scFv (JCAR021) in adults with R/R B-ALL (NCT03103971). Twenty-three patients received lymphodepletion chemotherapy and JCAR021 infusion. Nineteen patients developed cytokine release syndrome (any grade, 83%; grade 2, 61%) and 12 developed neurotoxicity (52%; grade ≥3, 35%). The overall response and complete response (CR)/CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) rates were 82% and 64%, respectively. We observed measurable residual disease-negative bone marrow (BM) responses in 82% of those with BM disease and extramedullary responses by positron emission tomography-computed tomography in 79% (CR, 50%) of those with measurable fluorodeoxyglucose-avid disease. The median duration of remission (DOR) was 10 months with a 4-year DOR probability of 29%. Four patients underwent allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation while in CR/CRi after JCAR021. Durable remissions were observed in patients with low BM disease burden. In contrast, the DOR was limited in those with high BM burden. We observed similar outcomes in CAR-naïve adult patients with B-ALL receiving CD19 CAR T cells expressing a fully human or murine scFv-containing CAR. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as #NCT03103971.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.G. reports consultancy with Kite, a Gilead company, MorphoSys, Legend Biotech, Janssen, and Sobi; received honoraria from Kite, a Gilead company, Legend Biotech, Janssen, and Sobi; received research funding from MorphoSys, Angiocrine Bioscience, CARGO Therapeutics, Celgene, a BMS company, CytoAgents, Faron Pharmaceuticals, Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company, and Sobi; and serves on an independent data review committee at Century Therapeutics. E.C.L. reports consultancy with Glass Health. E.L.K. received research funding from Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company. A.V.H. received honoraria from Novartis, BMS, and Nektar Therapeutics; and research funding from BMS, Nektar Therapeutics, and Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company. S.F. filed and received license fees on patents for optimizing CAR T-cell function; received research funding from BMS; and reports consultancy with Prescient Therapeutics. M.S. reports consultancy with Fate Therapeutics, Genmab, MorphoSys/Incyte, Eli Lilly, BMS, Genentech, Kite, a Gilead company, AbbVie, Mustand Bio, ADC Therapeutics, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics, Janssen, MEI Pharma, and Regeneron; and received research funding from Genmab, Vincerx, MorphoSys/Incyte, BMS, Genentech, AbbVie, Mustang Bio, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics, and TG Therapeutics. R.D.C. reports consultancy with Amgen, Pfizer, Jazz, and Kite, a Gilead company/Gilead; received honoraria from Amgen, Autolus, Pfizer, Jazz, and Kite, a Gilead company/Gilead; received research funding from Amgen, Merck, Incyte, Pfizer, Servier, Kite, a Gilead company/Gilead, and Vanda Pharmaceuticals; has membership on the board of directors or advisory committees at Autolus and PeproMene Bio; and has a spouse who was employed by and owned stock in Seagen within the last 24 months. S.R.R. is the cofounder of Lyell Immunopharma and Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company; received research funding from Lyell Immunopharma and BMS; has an intellectual property license agreement with Lyell Immunopharma and BMS; serves on advisory boards at Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company and Adaptive Biotechnologies; and is a member of board of directors at Ozette Technologies. D.G.M. reports consultancy with A2 Biotherapeutics, Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Mustang Bio, Novartis, Incyte, Gilead Sciences, Kite, a Gilead company, a Gilead Sciences, Pharmacyclics, Umoja, Celgene, a BMS company, Genentech, MorphoSys, BMS, Amgen, Navan Technologies, and Bioline Rx; is a current holder of stock options in privately held companies A2 Biotherapeutics and Navan Technologies; received honoraria from A2 Biotherapeutics, Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Mustang Bio, Novartis, Incyte, Gilead Sciences, Kite, a Gilead company, a Gilead Sciences, Pharmacyclics, Umoja, Celgene, a BMS company, Genentech, MorphoSys, BMS, Amgen, and Navan Technologies; serves as a member of the scientific advisory Boards at A2 Biotherapeutics, Navan Technologies, and Chimeric Therapeutics; has rights to royalties from Fred Hutch for patents licensed to Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company; received research funding from Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company, Legend Biotech, Kite, a Gilead company, a Gilead Sciences, Celgene, a BMS company, and BMS; is a member of the CAR T steering committee at Lyell Immunopharma; is a member of the scientific review committee of Gilead Sciences; is a part of the Research Scholars Program in Hematologic Malignancies at Gilead Sciences; reports membership on board of directors or advisory committees and participation on data safety monitory boards at Celgene, a BMS company and Bioline Rx; is chair and member of the lymphoma steering committee at Genentech; is a member of the JCAR017 EAP-001 safety review committee, member of the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Strategic Council, and member of the JCAR017-BCM-03 scientific steering committee under BMS; is a member of the clinical advisory board, CD19/CD20 bispecific CAR T-Cell Therapy Program at ImmPACT Bio; and a member of the clinical advisory board at Interius. C.J.T. received research funding from Juno Therapeutics, a BMS company, Nektar Therapeutics, and 10x Genomics; serves on scientific advisory boards at Caribou Biosciences, T-CURX, Myeloid Therapeutics, ArsenalBio, Cargo Therapeutics, Celgene, a BMS company Cell Therapy, Differentia Bio, eGlint, and Advesya; is a data safety monitory board member at Kyverna; reports ad hoc advisory roles/consulting (last 12 months with Prescient Therapeutics, Century Therapeutics, IGM Biosciences, AbbVie, Boxer Capital, Novartis, and Merck Sharp & Dohme; has stock options in Eureka Therapeutics, Caribou Biosciences, Myeloid Therapeutics, ArsenalBio, Cargo Therapeutics, and eGlint; reports speaker engagement (last 12 months) with Pfizer and Novartis; and is an inventor on patents related to CAR T-cell therapy. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Humanizing CAR T-cell therapy in B-ALL.Blood Adv. 2025 Apr 22;9(8):1916-1917. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015852. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 40214999 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of CD19 CAR T constructed with a new anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor in relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Sep 7;13(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00953-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32894185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Humanized CD19 CAR-T cells in relapsed/refractory B-ALL patients who relapsed after or failed murine CD19 CAR-T therapy.BMC Cancer. 2022 Apr 12;22(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09489-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35410148 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Engineered Universal CD19/CD22 Dual-Targeted CAR-T Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 May 15;27(10):2764-2772. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3863. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33627493 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment with anti CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells after antibody-based immunotherapy in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Jan;68(1):17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2019.12.001. Epub 2019 Dec 25. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31882377 Review.
-
Advances in the development of chimeric antigen receptor-T-cell therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Feb 20;133(4):474-482. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000638. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 31977556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Humanizing CAR T-cell therapy in B-ALL.Blood Adv. 2025 Apr 22;9(8):1916-1917. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015852. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 40214999 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ghorashian S, Kramer AM, Onuoha S, et al. Enhanced CAR T cell expansion and prolonged persistence in pediatric patients with ALL treated with a low-affinity CD19 CAR. Nat Med. 2019;25(9):1408–1414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

