Relationship between additional mutations at diagnosis and treatment response in patients with essential thrombocythemia
- PMID: 39820709
- PMCID: PMC11950951
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014791
Relationship between additional mutations at diagnosis and treatment response in patients with essential thrombocythemia
Abstract
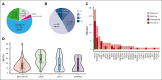
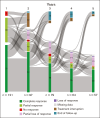
Patients with essential thrombocythemia (ET) have a chronic evolution with a risk of hematologic transformation associated with a dismal outcome. Because patients with resistance or intolerance have adverse prognosis, it is important to identify which patient will respond to first-line treatment. We, therefore, aim to describe the association between additional mutations and response to first-line treatment in patients with ET. In this retrospective study, we analyzed the molecular landscape of 121 ET patients first-line treated with hydroxyurea (HU; n = 86) or pegylated interferon (peg-IFN; n = 35). Patients undergoing peg-IFN therapy were younger and had higher proportion of low and very low risk of thrombosis recurrence. A total of 62 patients (51%) had ≥1 additional mutations at diagnosis. At 12 months of treatment, 75 patients (62%) achieved complete response (CR), 37 (31%) partial response, and 7 (6%) no response. The presence of at least 1 additional mutation at diagnosis was associated with not achieving CR (hazard ratio [HR], 0.65; P = .038), whereas treatment with peg-IFN was associated with higher CR (HR, 2.00; P = .002). The number of additional mutations at diagnosis was associated with hematologic progressions (P < .0001). None of the patients receiving peg-IFN therapy progressed to myelofibrosis, whereas 16 of 86 patients (19%) treated with HU developed secondary myelofibrosis. In conclusion, our results suggest that the presence of at least 1 additional mutation at diagnosis is associated with failure to achieve CR and also with an increased risk of hematologic evolution.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic J-P, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434(7037):1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1779–1790. - PubMed
-
- Klampfl T, Gisslinger H, Harutyunyan AS, et al. Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(25):2379–2390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

