Preventive and curative dental services utilization among children aged 12 years and younger in Tehran, Iran, based on the Andersen behavioral model: A generalized structural equation modeling
- PMID: 39820811
- PMCID: PMC11737785
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312043
Preventive and curative dental services utilization among children aged 12 years and younger in Tehran, Iran, based on the Andersen behavioral model: A generalized structural equation modeling
Abstract
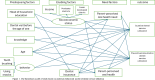
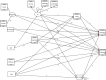
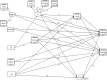
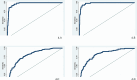
World Health Organization invites the nations to progress towards universal health care coverage. This study evaluated preventive and curative dental services utilization among children aged 12 years and younger in Tehran, Iran, based on the Andersen behavioral model using a generalized structural equation modeling. A phone-based cross-sectional study was conducted in Tehran, Iran, on 886 children in 2023. Information on curative and preventive/consultation dental service utilization and associated factors was collected by a standard questionnaire. We used a generalized structural equation model (GSEM) to build a model based on Andersen's behavioral model. Of 886 children, 22.1% used curative dental services, and 19.9% used preventive/consultation services in the past year. Among children aged 6 years and younger, age (OR = 1.87, p-value <0.001) and parent-perceived oral health need (OR = 54.77, p-value <0.001) predicted curative services utilization and age (OR = 1.45, p-value <0.001), knowledge (OR = 1.36, p-value <0.001), dental visit before the age of one (OR = 6.05, p-value = 0.04), and socioeconomic status (OR = 1.65, p-value = 0.03) predicted preventive/consultation services utilization. Regarding children aged 7 to 12, knowledge (OR = 1.28, p-value = 0.03), dental visit before the age of one (OR = 11.12, p-value = 0.02), socioeconomic status (OR = 2.53, p-value = 0.01), dental insurance (OR = 4.17, p-value <0.001), and parent-perceived oral health need (OR = 19.48, p-value <0.001) associated with curative dental services utilization, and dental visit before the age of one (OR = 10.05, p-value = 0.02), oral health behavior (OR = 1.25, p-value = 0.04), socioeconomic status (OR = 3.74, p-value <0.001), and parent-perceived oral health need (OR = 4.62, p-value <0.001) related to preventive/consultation services utilization. The findings of this study underscore the significant influence of predisposing, enabling, and need factors on dental services utilization among children aged 12 years and younger. These results provide a valuable perspective for policymakers, highlighting the modifiable determinants that could be targeted to improve dental services utilization in this age group.
Copyright: © 2025 Amirian et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
he authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utilization of dental services and associated factors among preschool children in China.BMC Oral Health. 2020 Jan 8;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0996-x. BMC Oral Health. 2020. PMID: 31914978 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and non-clinical variables associated with preventive and curative dental service utilisation: a cross-sectional study among adolescents and young adults in Central Mexico.BMJ Open. 2019 Sep 18;9(9):e027101. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027101. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31537556 Free PMC article.
-
Oral health need and access to dental services: evidence from the National Survey of Children's Health, 2007.Matern Child Health J. 2012 Apr;16 Suppl 1:S27-34. doi: 10.1007/s10995-012-0992-0. Matern Child Health J. 2012. PMID: 22456986
-
Patterns of preventive dental behavior.Public Health Rep. 1986 Mar-Apr;101(2):175-84. Public Health Rep. 1986. PMID: 3083472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Utilization of dental services for children: a review of the influencing factors and the possible improvements].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 May 9;52(5):324-328. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2017.05.014. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28482452 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Organization WH. Health in 2015: from MDGs, millennium development goals to SDGs, sustainable development goals. 2015.
-
- Curi DSC, Figueiredo ACL, Jamelli SR. Factors associated with the utilization of dental health services by the pediatric population: an integrative review. Cien Saude Colet. 2018;23(5):1561–76. - PubMed
-
- Aqeeli A. Predictors of Dental Care Utilization in School Children in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Int J Dent Oral Sci. 2021:5027–32.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

