Functional alignment in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformity achieves safe coronal alignment and excellent short-term outcomes
- PMID: 39821487
- PMCID: PMC12104782
- DOI: 10.1002/ksa.12585
Functional alignment in robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformity achieves safe coronal alignment and excellent short-term outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: Functional alignment (FA) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) prioritizes soft tissue balancing and anatomical restoration without systematic correction to neutral alignment. Most studies have focused on varus deformity, with little evidence available about FA in valgus deformity. The hypothesis of the present study was that FA in robotic-assisted TKA for valgus deformity would demonstrate correction of the coronal alignment and yield satisfactory short-term outcomes.
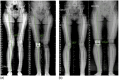
Methods: This retrospective study included 58 patients with valgus coronal alignment (hip-knee-angle [HKA] ≥ 183°) who underwent robotic-assisted TKA using the FA technique with a minimum of 1-year follow-up. Outcomes were assessed through the Knee Society Score (KSS), Oxford Knee Score (OKS), Forgotten Joint Score (FJS) and radiographic measurements of alignment and phenotypes. Complication and revision rates were also analyzed.
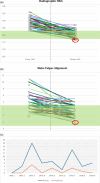
Results: The cohort included 39 females and 19 males with a median age of 70. Post-operatively, 86.2% of cases achieved coronal alignment within the safe zone (HKA 177-183°). Significant improvements were observed in KSS (part 1: 69.5-95, part 2: 65-94, p < 0.001), while OKS and FJS exhibited optimal outcomes. Two complications were recorded: one aseptic loosening (1.7%) and one early infection (1.7%). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated favourable implant survivorship at a median follow-up of 18 months.
Conclusion: FA in image-based robotic TKA is a safe and effective approach for patients with valgus deformity. This procedure resulted in a modest correction of the coronal alignment, where no soft tissue releases were needed. The majority of the cases fell within the target coronal alignment boundaries by only accommodating the individual laxities, suggesting the aim of FA to restore each knee's pre-pathological alignment.
Level of evidence: Level IV.
Keywords: functional alignment; knee phenotype; robotic knee replacement; valgus knee.
© 2025 The Author(s). Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Cécile Batailler: Consultant for Smith and Nephew and Stryker. Elvire Servien: Consultant for Smith and Nephew. Sébastien Lustig: Consultant for Heraeus, Stryker, Depuy Synthes, Smith and Nephew. Institutional research support to Lepine and Amplitude. Editorial Board for Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (Am). The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tibial implant varus >3° does not adversely affect outcomes or revision rates in functionally aligned image-based robotic total knee arthroplasty in a minimum of 2-year follow-up.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025 Aug;33(8):2917-2927. doi: 10.1002/ksa.12659. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025. PMID: 40130488
-
Imageless robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty allows intra-articular correction of severe extra-articular deformities using functional alignment and desired under-correction.Int Orthop. 2025 Aug;49(8):1869-1878. doi: 10.1007/s00264-025-06563-8. Epub 2025 May 22. Int Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40402236
-
Effect of inverse kinematic alignment total knee arthroplasty on coronal alignment of the ankle joint in patients with varus knee deformity.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Sep;144(9):4455-4461. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05549-2. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39271492 Free PMC article.
-
Component placement accuracy in two generations of handheld robotics-assisted knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021 Dec;141(12):2059-2067. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-04040-6. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. PMID: 34304279 Review.
-
Robotic-assisted hip and knee revision arthroplasty: A scoping review.J Exp Orthop. 2025 May 26;12(2):e70285. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70285. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40421409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral approach in robotic total knee arthroplasty for valgus knees: A step-by-step technique.SICOT J. 2025;11:20. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2025017. Epub 2025 Mar 27. SICOT J. 2025. PMID: 40145785 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the coronal plane in robotic total knee arthroplasty-Part 1: Variations in tibial slope and distal femoral flexion do not affect outcomes.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025 Aug;33(8):2928-2938. doi: 10.1002/ksa.12658. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025. PMID: 40130477 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral approach for total knee arthroplasty in patients with valgus deformity: A step-by-step surgical technique.SICOT J. 2025;11:51. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2025047. Epub 2025 Sep 1. SICOT J. 2025. PMID: 40889350 Free PMC article.
-
Cementless versus cemented fixation in image-based robotic total knee arthroplasty guided by functional knee positioning principles.SICOT J. 2025;11:32. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2025027. Epub 2025 May 27. SICOT J. 2025. PMID: 40421867 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of joint deformity after MIPPO with double reverse traction repositor based on Hounsfield units derived from CT scans.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jul 8;20(1):621. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06010-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40629446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batailler C, Fernandez A, Swan J, Servien E, Haddad FS, Catani F, et al. MAKO CT‐based robotic arm‐assisted system is a reliable procedure for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(11):3585–3598. - PubMed
-
- Bertugli E, Zambianchi F, Batailler C, Bazzan G, Lustig S, Catani F. Change of CPAK class does not affect functional outcomes in robotic arm‐assisted total knee arthroplasty performed with functional alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024. - PubMed
-
- Bonner TJ, Eardley WGP, Patterson P, Gregg PJ. The effect of post‐operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow‐up of 15 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93–B(9):1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Chelli S, Rudyy T, Avram GM, Huegli RW, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT. Gender‐based differences exist in the functional knee phenotypes classification of the osteoarthritic knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2024;32(10):2505–2515. - PubMed
-
- Clement ND, Scott CEH, Hamilton DF, MacDonald D, Howie CR. Meaningful values in the Forgotten Joint Score after total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2021;103–B(5):846–854. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

