Temporal changes and implications of diffusion tensor imaging metrics and cerebral white matter volume in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy - a prospective study
- PMID: 39821632
- PMCID: PMC12041146
- DOI: 10.1007/s00234-024-03527-4
Temporal changes and implications of diffusion tensor imaging metrics and cerebral white matter volume in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy - a prospective study
Abstract
Aims: To test utility of diffusion MRI-derived indices in carotid endarterectomy (CEA), change of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics, cerebral white matter (WM) volumes were evaluated and predictors of overall mortality determined.
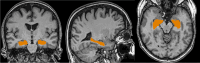
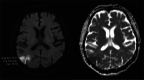
Methods: Prospectively enrolled participants had preoperative, immediate and late postoperative DTI after CEA. WM volumes, DTI metrics (fractional anisotropy, FA; axial, radial, mean diffusivities; AD, RD, MD, respectively) were calculated for the index/contralateral hemispheres at all time points. Temporal changes, predictors of log2-transformed WM volumes, DTI values were analyzed using linear mixed model. Uni- and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to identify predictors of mortality.
Results: 60 subjects (57% male, 69.5 ± 7.2years) were included. Significantly increased AD and MD was observed in both hemispheres comparing the preoperative and immediate postoperative DTI metrics (index AD: β = 0.02 [95%CI:0.01,0.02], p < 0.001; index MD: β = 0.02 [95%CI:0.01,0.03], p < 0.001; contralateral AD: β = 0.01 [95%CI:0.01,0.02], p = 0.001; contralateral MD: β = 0.02 [95%CI:0.01,0.03], p = 0.003). The index MD decreased (β = 0.01 [95%CI:0.01,0.001], p = 0.04), bilateral WM volumes (index WM: β = 0.04 [95%CI:0.02,0.07], p < 0.001; contralateral WM: β = 0.05 [95%CI:0.03,0.07], p < 0.001) decreased significantly between the immediate and late postoperative scans. Postoperative contralateral FA correlated significantly with lower mortality (HR = 0.001 [95%CI:0.001,0.19], p = 0.02); postoperative contralateral RD (HR = 3.74 × 104 [95%CI:1.62,8.60 × 108], p = 0.04) and MD (HR = 1.19 × 105 [95%CI:1.03,1.37 × 1010], p = 0.049) were significant predictors of mortality.
Conclusion: The increase of various DTI metrics from pre-to-postoperative may be indicative of microstructural deterioration following CEA. Temporal changes between the immediate and late postoperative scans suggest, however, reversal of detrimental WM changes and clearance of presumed subclinical WM edema. Our results also imply, that preserved cerebral properties are protective after CEA.
Keywords: Carotid artery stenosis; Carotid endarterectomy; Diffusion MRI; Diffusion tensor imaging; Mortality.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Institutional Ethical Committee (IV/667-1/2022/EKU). Informed consent: Written informed consent was signed prior to enrollment and all imaging studies. Conflicts of interest: Nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Postoperative increase in cerebral white matter fractional anisotropy on diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging is associated with cognitive improvement after uncomplicated carotid endarterectomy: tract-based spatial statistics analysis.Neurosurgery. 2013 Oct;73(4):592-8; discussion 598-9. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000013. Neurosurgery. 2013. PMID: 23756737
-
Postoperative cerebral white matter damage associated with cerebral hyperperfusion and cognitive impairment after carotid endarterectomy: a diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;34(5-6):358-67. doi: 10.1159/000343505. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 23154793
-
Mid-term effects of carotid endarterectomy on cognition and white matter status evaluated by whole brain diffusion tensor imaging metrics: A preliminary analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Jun;151:110314. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110314. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35452954
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
-
A systematic review of microstructural abnormalities in multiple sclerosis detected with NODDI and DTI models of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Dec;104:61-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2023.09.010. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37775062
References
-
- Mathiesen EB, Waterloo K, Joakimsen O, Bakke SJ, Jacobsen EA, Bonaa KH (2004) Reduced neuropsychological test performance in asymptomatic carotid stenosis: the Tromso Study. Neurology 62:695–701 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

