Plasma proteomic biomarkers as mediators or moderators for the association between poor cardiovascular health and white matter microstructural integrity: The UK Biobank study
- PMID: 39822062
- PMCID: PMC11864230
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14507
Plasma proteomic biomarkers as mediators or moderators for the association between poor cardiovascular health and white matter microstructural integrity: The UK Biobank study
Abstract
Introduction: The plasma proteome's mediating or moderating roles in the association between poor cardiovascular health (CVH) and brain white matter (WM) microstructural integrity are largely unknown.
Methods: Data from 3953 UK Biobank participants were used (40-70 years, 2006-2010), with a neuroimaging visit between 2014 and 2021. Poor CVH was determined using Life's Essential 8 (LE8) and reversing standardized z-scores (LE8z _rev). The plasma proteome was examined as a potential mediator or moderator of LE8z _rev's effects on quantitative diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) metrics.
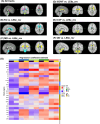
Results: LE8z_rev was significantly associated with deteriorated WM microstructural integrity, as reflected by lower tract-averaged fractional anisotropy (dMRI-FAmean), (β ± standared error (SE): -0.00152 ± 0.0003, p < 0.001) and higher tract-averaged orientation dispersion (dMRI-ODmean), (β ± SE:+0.00081 ± 0.00017, p < 0.001). Ten strongly mediating plasma proteins of 1463 were identified, with leptin as the principal driver.
Discussion: Poor CVH is linked to poor WM microstructural integrity measures (lower FAmean and higher ODmean), mostly mediated through leptin.
Highlights: Up to 3953 UK Biobank participants were selected for this study. Poor cardiovascular health (CVH) was determined using Life's Essential 8. The plasma proteome was examined as a potential mediator or moderator of poor CVH's effect on dMRI metrics. Ten plasma proteins were identified with strong mediating effects, with leptin being the principal driver.
Keywords: Life's Essential 8; aging; cardiovascular health; diffusion‐weighted magnetic resonance imaging; plasma proteomic biomarkers; white matter microstructural integrity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures


References
-
- Guerchet M, Prince M, Prina M. Numbers of people with dementia worldwide: An update to the estimates in the World Alzheimer Report 2015. Alzheimer's Disease International; 2020.
-
- Alzheimer's Association . 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(4):1598‐1695. - PubMed
-
- Sosa‐Ortiz AL, Acosta‐Castillo I, Prince MJ. Epidemiology of dementias and Alzheimer's disease. Arch Med Res. 2012;43:600‐608. - PubMed
-
- Lindeboom J, Weinstein H. Neuropsychology of cognitive ageing, minimal cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's disease, and vascular cognitive impairment. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;490:83‐86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

