Impact of Surgical Mask Placement Over High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Oxygenation Parameters in COVID-19 Patients Experiencing Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
- PMID: 39822415
- PMCID: PMC11738091
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75871
Impact of Surgical Mask Placement Over High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Oxygenation Parameters in COVID-19 Patients Experiencing Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
Abstract
Background: During the COVID-19 pandemic, managing respiratory failure in critically ill patients has presented significant challenges. A high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) has been established as an effective respiratory support modality, offering heated, humidified oxygen at high flow rates. However, concerns persist regarding the potential for aerosol dispersion and the risk of viral transmission, particularly in COVID-19. This study investigates the impact of surgical mask (3-ply surgical mask) placement over HFNC on oxygenation parameters in COVID-19 patients experiencing hypoxemic respiratory failure.
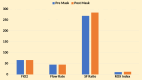
Methods: A retrospective analysis of clinical data from a tertiary medical facility was conducted. The study included 35 patients with confirmed COVID-19 and moderate to severe hypoxemia. Oxygenation indices such as the SpO2/FiO2 (SF) ratio, flow rate, and the ratio of oxygen saturation index (ROX index) were monitored before and after the application of surgical masks over HFNC. Statistical analyses were performed to compare these parameters before and after surgical mask placement.
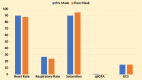
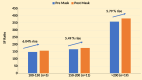
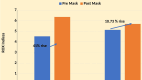
Results: The adjunctive use of surgical masks over HFNC significantly improved oxygenation parameters compared to HFNC alone. Despite these improvements, there was no significant change in heart and respiratory rates, quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) scores, or Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) levels. Subgroup analysis showed an increase in SF ratio ranging between 5.49% and 6.04% in patients with ROX indices, but these trends were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: This study provides preliminary evidence that surgical masks over HFNC may enhance oxygenation in critically ill COVID-19 patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure. These results underscore the potential importance of infection control measures in respiratory therapy during pandemics and suggest that further investigation in more extensive prospective studies is warranted.
Keywords: covid-19; high flow nasal cannula (hfnc); hypoxemia respiratory failure; quick sequential organ failure assessment (qsofa); rox index.
Copyright © 2024, Coatwala et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC) of Mahatma Gandhi Mission Medical College issued approval DHR-EC/2022/03/03. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy to treat patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure consequent to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Vianello A, Arcaro G, Molena B, et al. Thorax. 2020;75:998–1000. - PubMed
-
- Predicting success of high-flow nasal cannula in pneumonia patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure: the utility of the ROX index. Roca O, Messika J, Caralt B, et al. J Crit Care. 2016;35:200–205. - PubMed
-
- An index combining respiratory rate and oxygenation to predict outcome of nasal high-flow therapy. Roca O, Caralt B, Messika J, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;1:1368–1376. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
