Preemptive hydromorphone analgesia reduces postoperative delirium and stress response in laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients
- PMID: 39822504
- PMCID: PMC11733323
- DOI: 10.62347/HFRZ2901
Preemptive hydromorphone analgesia reduces postoperative delirium and stress response in laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effects of preemptive hydromorphone analgesia on postoperative delirium and stress response in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted, including 167 patients who underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy at Xi'an Central Hospital between June 2021 and November 2023. Patients were categorized into an observation group (n=87) receiving preemptive hydromorphone hydrochloride analgesia and a control group (n=80) without preemptive analgesia. Postoperative pain was assessed using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), and stress response was evaluated by measuring epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine levels. The incidence of postoperative delirium was recorded. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify risk factors for postoperative delirium.
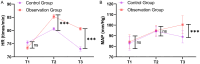
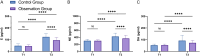
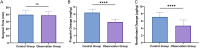
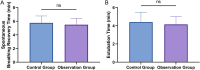
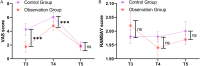
Results: The VAS score at 30 minutes postoperative was significantly lower in the observation group than that in the control group (P<0.001). Similarly, postoperative levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine were significantly reduced in the observation group (all P<0.001). The incidence of postoperative delirium was also significantly lower in the observation group (P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified higher doses of propofol (P<0.001; odds ratio =3.102, 95% confidence interval: 1.144-9.777) and remifentanil (P=0.001; odds ratio =2.376, 95% confidence interval: 1.469-4.290) as independent risk factors for postoperative delirium, indicating a significant increase in delirium risk with higher drug doses.
Conclusion: Preemptive hydromorphone analgesia significantly alleviates postoperative pain, reduces stress responses, and lowers the incidence of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Compared to conventional analgesia strategies, hydromorphone provides superior pain control and a favorable safety profile.
Keywords: Hydromorphone hydrochloride; laparoscopic cholecystectomy; postoperative delirium; preemptive analgesia; stress response.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preemptive analgesia for postoperative pain relief in thoracolumbosacral spine operations: a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial.J Neurosurg Spine. 2018 Dec 1;29(6):647-653. doi: 10.3171/2018.5.SPINE171380. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018. PMID: 30215593 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy of Pregabalin and Gabapentin for Preemptive Analgesia in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomised Double-Blind Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 9;15(10):e46719. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46719. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021908 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of single-dose preemptive intravenous ibuprofen on postoperative opioid consumption and acute pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Feb;96(8):e6200. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006200. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28225506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Different Preemptive Analgesia Measures in Pain Management after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pain Ther. 2024 Dec;13(6):1471-1497. doi: 10.1007/s40122-024-00647-w. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Pain Ther. 2024. PMID: 39227523 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Review of Intrathecal Hydromorphone Dose Range and Complications.Pain Physician. 2023 Sep;26(5):E557-E565. Pain Physician. 2023. PMID: 37774193 Review.
References
-
- Romucho Aguilar FB, Zapata Ormeño GC, Alzamora de Los Godos Urcia LA, Calderón Saldaña JP, Ausejo Galarza JR. Efficacy of mini-laparoscopic cholecystectomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2023;115:521. - PubMed
-
- Xuan C, Yan W, Wang D, Li C, Ma H, Mueller A, Chin V, Houle TT, Wang J. Efficacy of preemptive analgesia treatments for the management of postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2022;129:946–958. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
