Efficacy of three predictive models for deep vein thrombosis in patients with lumbar disc herniation
- PMID: 39822564
- PMCID: PMC11733348
- DOI: 10.62347/TWTG6803
Efficacy of three predictive models for deep vein thrombosis in patients with lumbar disc herniation
Abstract
Objective: To develop predictive models for assessing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) risk among lumbar disc herniation (LDH) patients and evaluate their performances.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 798 LDH patients treated at the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University from January 2017 to December 2023. The patients were divided into a training set (n = 558) and a test set (n = 240) using computer-generated random numbers in a ratio of 7:3. Patients without DVT in the training set were categorized as the non-DVT group (n = 463), while those diagnosed with DVT were the DVT group (n = 95). Univariate analysis was performed to compare clinical data between the two groups. Data with statistical significance were used for the development of a Logistic regression model, Gradient boosting model, and Random Forest model. Model performance was evaluated through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and calibration curve assessment.
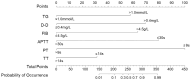
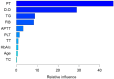
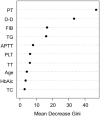
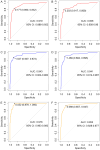
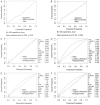
Results: In the training set, univariate analysis revealed significant differences in age, platelets (PLT), cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), glycated hemoglobin (HbAlc), D-dimer (D-D), fibrinogen (FIB), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), and thrombin time (TT) between the non-DVT group and the DVT group (all P<0.05). Predictive models were constructed based on these indicators. The areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) in the training set were as follows (in descending order): Random Forest model (0.978) > Gradient boosting model (0.943) > Logistic regression model (0.919). In the test set, the AUCs were: Random Forest model (0.952) > Gradient boosting model (0.941) > Logistic regression model (0.908). The DeLong test indicated that the AUC of the Random Forest model in the training set was significantly higher than that of the Logistic regression model (P<0.05); however, no significant difference was observed between the other two models. Calibration curves demonstrated that the predictive probabilities from all three models closely aligned with actual DVT incidence in both sets.
Conclusion: The Logistic regression model, Gradient boosting model, and Random Forest model constructed in this study exhibit good predictive value for the occurrence of DVT in LDH patients, aiding in the optimization of clinical management of clinical management. Among them, the Random Forest model performed the best of the three.
Keywords: Gradient boosting model; Logistic regression model; Lumbar disc herniation; Random Forest model; deep vein thrombosis; risk factor.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Predictive value of combined examination of coagulation and fibrinolysis indexes for deep venous thrombosis after proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in elderly patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025 Apr 25;38(4):371-7. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.20231098. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025. PMID: 40296598 Chinese.
-
Study on risk factors of preoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients with lower limb fractures and construction and validation of risk prediction nomogram model.BMC Surg. 2024 Dec 21;24(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02718-3. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 39709353 Free PMC article.
-
[Incidence and risk factor analysis of deep venous thrombosis in patients with severe traumatic brain injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):182-186. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827306 Chinese.
-
[Predictive value of D-dimer for deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity in adult burn patients].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 Apr 20;38(4):335-340. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20201021-00444. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35462511 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Development and validation of a prediction model for coronary heart disease risk in depressed patients aged 20 years and older using machine learning algorithms.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 9;11:1504957. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1504957. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39850379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basindwah S, AlHamzah M, Balsharaf F, AlRajhi B, Sewaralthahab S, Altoijry A, Altuwaijri T, Al-Habib A. Prevalence of asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis in preoperative state of spine surgeries. World Neurosurg. 2023;170:e737–e743. - PubMed
-
- Kafeza M, Shalhoub J, Salooja N, Bingham L, Spagou K, Davies AH. A systematic review of clinical prediction scores for deep vein thrombosis. Phlebology. 2017;32:516–531. - PubMed
-
- He SY, Zhang P, Qin HJ, Jiang N, Yu B. Incidence and risk factors of preoperative deep venous thrombosis following hip fracture: a retrospective analysis of 293 consecutive patients. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48:3141–3147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
