Disseminated intravascular coagulation: cause, molecular mechanism, diagnosis, and therapy
- PMID: 39822757
- PMCID: PMC11733103
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70058
Disseminated intravascular coagulation: cause, molecular mechanism, diagnosis, and therapy
Abstract
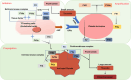
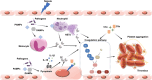
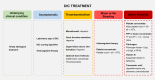
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a complex and serious condition characterized by widespread activation of the coagulation cascade, resulting in both thrombosis and bleeding. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of DIC, emphasizing its clinical significance and the need for improved management strategies. We explore the primary causes of DIC, including sepsis, trauma, malignancies, and obstetric complications, which trigger an overactive coagulation response. At the molecular level, DIC is marked by excessive thrombin generation, leading to platelet and fibrinogen activation while simultaneously depleting clotting factors, creating a paradoxical bleeding tendency. Diagnosing DIC is challenging and relies on a combination of existing diagnostic criteria and laboratory tests. Treatment strategies focus on addressing the underlying causes and may involve supportive care, anticoagulation therapy, and other supportive measures. Recent advances in understanding the pathophysiology of DIC are paving the way for more targeted therapeutic approaches. This review highlights the critical need for ongoing research to enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy, ultimately improving patient outcomes in those affected by DIC.
Keywords: coagulation; disseminated intravascular coagulation; fibrinolysis; sepsis; trauma.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation and its immune mechanisms.Blood. 2022 Mar 31;139(13):1973-1986. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007208. Blood. 2022. PMID: 34428280 Free PMC article.
-
[A novel molecular marker for thrombus formation and life prognosis--clinical usefulness of measurement of soluble fibrin monomer-fibrinogen complex (SF)].Rinsho Byori. 2004 Apr;52(4):355-61. Rinsho Byori. 2004. PMID: 15164605 Review. Japanese.
-
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: An Update on Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Strategies.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018 Dec;24(9_suppl):8S-28S. doi: 10.1177/1076029618806424. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018. PMID: 30296833 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical practice guidelines for management of disseminated intravascular coagulation in Japan 2024: significance of guidelines developed for each underlying disease.Int J Hematol. 2025 May;121(5):586-591. doi: 10.1007/s12185-025-03928-y. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Int J Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39954183 Review.
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation: epidemiology, biomarkers, and management.Br J Haematol. 2021 Mar;192(5):803-818. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17172. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 33555051 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of ADR reports of cetuximab based on the FDA adverse event reporting system database.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 3;15(1):4104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88838-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39901061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelborg K, Larsen JB, Hvas AM. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: epidemiology, biomarkers, and management. British journal of haematology. 2021;192(5):803‐818. - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Zhang B, Shen Y, Li J, Yuan X, Tang N. Validation of two revised, simplified criteria for assessing sepsis‐associated disseminated intravascular coagulation in ICU patients with sepsis‐3: a retrospective study. Laboratory medicine. 2023;54(3):291‐298. - PubMed
-
- Singh B, Hanson AC, Alhurani R, et al. Trends in the incidence and outcomes of disseminated intravascular coagulation in critically ill patients (2004‐2010): a population‐based study. Chest. 2013;143(5):1235‐1242. - PubMed
-
- Papageorgiou C, Jourdi G, Adjambri E, et al. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: an update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis: Official Journal of the International Academy of Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 2018;24(_suppl9):8s‐28s. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
