How Do Victimized Youth Emotionally and Socially Appraise Common Ways Third-Party Peers Intervene?
- PMID: 39823060
- PMCID: PMC11737377
- DOI: 10.1007/s10826-022-02285-2
How Do Victimized Youth Emotionally and Socially Appraise Common Ways Third-Party Peers Intervene?
Abstract
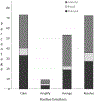
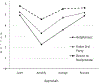
Adolescents targeted for peer aggression are at risk of emotion dysregulation and social withdrawal-responses that predict increased victimization and impede the protective factors of peer support. This study examined victimized youth's emotions and social appraisals following four common third-party peer actions. African American, European American, Mexican American, and Native American adolescents (N = 257, 53% female, M age = 15 years) described their emotions and appraisals of third-party peer actions after the participants had been targets of peer aggression. As hypothesized, emotional well-being, indexed by low levels of internalizing emotions and high levels of positive emotions, was greater after third-parties tried to help participants calm their emotions and resolve problems than after third-parties amplified participants' anger or avenged the victimized participants. Emotional well-being was greater after third-party revenge than after third-parties amplified participants' anger. Participants also reported calming, resolving and to a lesser extent third-party revenge, were more helpful, valued, and evoked a greater desire to reciprocate than anger amplification. Few ethnic differences were found. We consider how positive emotions and social appraisals of third-party actions are likely to increase well-being for victimized youth. The findings emphasize the need for specificity in how researchers and practitioners categorize third-party peer actions. Encouraging the types of action that are most appreciated by victimized youth might help adolescents be more effective sources of support in the context of peer aggression.
Keywords: Emotion regulation; Ethnically diverse; Peer support; Peer victimization; Third-party actions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gratitude for Bystander Action Varies by Peer Intervention and Social Norms.School Psych Rev. 2025;54(1):98-104. doi: 10.1080/2372966x.2023.2236008. Epub 2023 Jul 16. School Psych Rev. 2025. PMID: 39822705 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnically Diverse Adolescents Recount Third-Party Actions That Amplify Their Anger and Calm Their Emotions After Perceived Victimization.J Adolesc Res. 2020 Jul;35(4):461-488. doi: 10.1177/0743558419864021. Epub 2019 Jul 22. J Adolesc Res. 2020. PMID: 39802221 Free PMC article.
-
Third-Party Intervention in Peer Victimization: Self-Evaluative Emotions and Appraisals of a Diverse Adolescent Sample.J Res Adolesc. 2020 Sep;30(3):633-650. doi: 10.1111/jora.12548. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Res Adolesc. 2020. PMID: 32030841 Free PMC article.
-
"I Felt Like a Hero:" Adolescents' Understanding of Resolution-Promoting and Vengeful Actions on Behalf of Their Peers.J Youth Adolesc. 2021 Mar;50(3):521-535. doi: 10.1007/s10964-020-01346-3. Epub 2020 Nov 24. J Youth Adolesc. 2021. PMID: 33231783 Free PMC article.
-
Poly-Victimization and Peer Harassment Involvement in a Technological World.J Interpers Violence. 2018 Mar;33(5):762-788. doi: 10.1177/0886260517744846. J Interpers Violence. 2018. PMID: 29411695
Cited by
-
Gratitude for Bystander Action Varies by Peer Intervention and Social Norms.School Psych Rev. 2025;54(1):98-104. doi: 10.1080/2372966x.2023.2236008. Epub 2023 Jul 16. School Psych Rev. 2025. PMID: 39822705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfieri S, Tagliabue S, Marta E, Aresi G, Lanz M, & Pozzi M (2018). Gratitude as a variable of mediation between parental support and self-esteem in adolescence. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 27(2), 1394–1401. 10.1007/s10826-017-1001-4. - DOI
-
- Arsenio WF, Gold J, & Adams E (2006). Children’s conceptions and displays of moral emotions. In Killen M & Smetana JG (Eds.), Handbook of Moral Development pp. 581–609. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials