Ribosomal s6 kinase is a mediator of aquaporin-2 S256 phosphorylation and membrane accumulation after EGFR inhibition with erlotinib
- PMID: 39823198
- PMCID: PMC12228059
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00353.2024
Ribosomal s6 kinase is a mediator of aquaporin-2 S256 phosphorylation and membrane accumulation after EGFR inhibition with erlotinib
Abstract
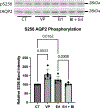
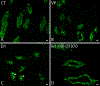
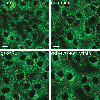
Vasopressin (VP) activates protein kinase A (PKA), resulting in phosphorylation events and membrane accumulation of aquaporin-2 (AQP2). Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition with erlotinib also induces AQP2 membrane trafficking with a phosphorylation pattern similar to VP, but without increasing PKA activity. Here, we identify the ribosomal s6 kinase (RSK) as a major mediator phosphorylating AQP2 in this novel, erlotinib-induced pathway. We found that RSK was expressed in collecting duct principal cells in rat kidneys. RSK inhibition with BI-D1870 blocked erlotinib-induced AQP2 serine 256 (S256) phosphorylation and membrane accumulation. CRISPR-generated RSK knockout (KO) cells failed to show increased S256 phosphorylation in response to erlotinib. Like PKA, RSK was able to phosphorylate AQP2 S256 in vitro. Inhibition of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1), a known activator of RSK, blocked erlotinib-induced AQP2 S256 phosphorylation and membrane accumulation. We conclude that RSK is a crucial terminal kinase phosphorylating AQP2 at S256 upon EGFR inhibition by erlotinib.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibition with erlotinib induces aquaporin-2 (AQP2) membrane accumulation with a phosphorylation pattern similar to vasopressin (VP). Here, we identify the ribosomal s6 kinase (RSK) as a major mediator phosphorylating AQP2 in this novel, erlotinib-induced pathway. In addition, we show that phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1), a known activator of RSK, is implicated in this pathway: PDK1 inhibition blocks erlotinib-induced AQP2 S256 phosphorylation and membrane accumulation.
Keywords: EGFR; aquaporin-2; epithelial transport; vasopressin; vesicle trafficking.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors.
Figures











References
-
- Olesen ETB, and Fenton RA. Aquaporin 2 regulation: implications for water balance and polycystic kidney diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 17: 765–781, 2021. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD021577/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- American Society of Nephrology (ASN)
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD032211/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096586/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10OD021577-01/HHS | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- DK096586/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- P30 DK057521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK057521/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- 1S10OD032211-01/HHS | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- P30 DK135043/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK043351/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

