NKAPL facilitates transcription pause-release and bridges elongation to initiation during meiosis exit
- PMID: 39824811
- PMCID: PMC11742055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55579-y
NKAPL facilitates transcription pause-release and bridges elongation to initiation during meiosis exit
Abstract
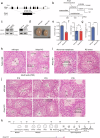
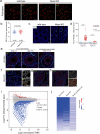
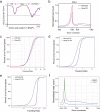
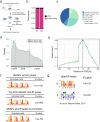
Transcription elongation, especially RNA polymerase II (Pol II) pause-release, is less studied than transcription initiation in regulating gene expression during meiosis. It is also unclear how transcription elongation interplays with transcription initiation. Here, we show that depletion of NKAPL, a testis-specific protein distantly related to RNA splicing factors, causes male infertility in mice by blocking the meiotic exit and downregulating haploid genes. NKAPL binds to promoter-associated nascent transcripts and co-localizes with DNA-RNA hybrid R-loop structures at GAA-rich loci to enhance R-loop formation and facilitate Pol II pause-release. NKAPL depletion prolongs Pol II pauses and stalls the SOX30/HDAC3 transcription initiation complex on the chromatin. Genetic variants in NKAPL are associated with azoospermia in humans, while mice carrying an NKAPL frameshift mutation (M349fs) show defective meiotic exit and transcriptomic changes similar to NKAPL depletion. These findings identify NKAPL as an R-loop-recognizing factor that regulates transcription elongation, which coordinates the meiotic-to-postmeiotic transcriptome switch in alliance with the SOX30/HDAC3-mediated transcription initiation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HDAC3 controls male fertility through enzyme-independent transcriptional regulation at the meiotic exit of spermatogenesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 May 21;49(9):5106-5123. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab313. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33939832 Free PMC article.
-
SPT6 functions in transcriptional pause/release via PAF1C recruitment.Mol Cell. 2022 Sep 15;82(18):3412-3423.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.06.037. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35973425 Free PMC article.
-
NELF Regulates a Promoter-Proximal Step Distinct from RNA Pol II Pause-Release.Mol Cell. 2020 Apr 16;78(2):261-274.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.02.014. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32155413 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4: a general regulator of transcription elongation.Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):70-81. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2108302. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 36047906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
7SKiing on chromatin: Move globally, act locally.RNA Biol. 2016 Jun 2;13(6):545-53. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1181254. Epub 2016 Apr 29. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27128603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harlen, K. M. & Churchman, L. S. The code and beyond: transcription regulation by the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol.18, 263–273 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Noe Gonzalez, M., Blears, D. & Svejstrup, J. Q. Causes and consequences of RNA polymerase II stalling during transcript elongation. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol.22, 3–21 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

