Neutralizing antibody immune correlates in COVAIL trial recipients of an mRNA second COVID-19 vaccine boost
- PMID: 39824819
- PMCID: PMC11748719
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55931-w
Neutralizing antibody immune correlates in COVAIL trial recipients of an mRNA second COVID-19 vaccine boost
Abstract
Neutralizing antibody titer has been a surrogate endpoint for guiding COVID-19 vaccine approval and use, although the pandemic's evolution and the introduction of variant-adapted vaccine boosters raise questions as to this surrogate's contemporary performance. For 985 recipients of an mRNA second bivalent or monovalent booster containing various Spike inserts [Prototype (Ancestral), Beta, Delta, and/or Omicron BA.1 or BA.4/5] in the COVAIL trial (NCT05289037), titers against 5 strains were assessed as correlates of risk of symptomatic COVID-19 ("COVID-19") and as correlates of relative (Pfizer-BioNTech Omicron vs. Prototype) booster protection against COVID-19 over 6 months of follow-up during the BA.2-BA.5 Omicron-dominant period. Consistently across the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine platforms and across all variant Spike inserts assessed, both peak and exposure-proximal ("predicted-at-exposure") titers correlated with lower Omicron COVID-19 risk in individuals previously infected with SARS-CoV-2, albeit significantly less so in naïve individuals [e.g., exposure-proximal hazard ratio per 10-fold increase in BA.1 titer 0.74 (95% CI 0.59, 0.94) for naïve vs. 0.41 (95% CI 0.23, 0.64) for non-naïve; interaction p = 0.013]. Neutralizing antibody titer was a strong inverse correlate of Omicron COVID-19 in non-naïve individuals and a weaker correlate in naïve individuals, posing questions about how prior infection alters the neutralization correlate.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: N.G.R. is a paid safety consultant for ICON, CyanVac, Imunon, and EMMES, and has served on selected advisory boards for Sanofi, Seqirus, Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. Emory receives funds for N.G.R. to conduct research from Sanofi, Lilly, Merck, Quidel, Immorna, Vaccine Company, and Pfizer-BioNTech. S.K. reports research support to his institution from Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, Bavarian Nordic, Meissa, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Institutes of Health. E.B.W. has served as an investigator for clinical trials or studies sponsored by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, Seqirus, Najit, and Clinetic; on advisory boards for Pfizer-BioNTech and Vaxcyte; as a consultant to IliAD Biotechnologies; and as a DSMB member for Shionogi. T.M.B. has served on an Advisory Board for Sanofi. D.N.F. has served on an Advisory Board for Gilead Sciences and for AXCELLA, and as site PI for clinical trials sponsored by Gilead Sciences, Regeneron, MetroBiotech LLC, and the NIH (DMID COVAIL). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
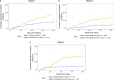
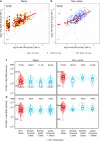

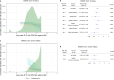

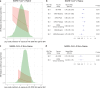


References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. COVID-19 vaccines. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-dise... (2024).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R37AI054165/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- UM1AI148684/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- contract 75N910D00024, task order 75N91022F00007/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- UM1 AI148685/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- C0000008/CL/CLC NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI148573/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI054165/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI148684/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93021C00014/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75A50122C00008/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA)
- Contract no. 75A50122C00008/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA)
- 75N93021D00021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- contract 75N910D00024, task order no. 75N91022F00007/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- 75N93021C00012/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

