Exploring technology acceptance of flight simulation training devices and augmented reality in general aviation pilot training
- PMID: 39824908
- PMCID: PMC11742415
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85448-7
Exploring technology acceptance of flight simulation training devices and augmented reality in general aviation pilot training
Abstract
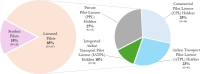
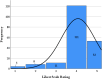
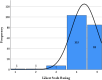
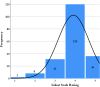
This study investigates pilot perspectives on the use of Flight Simulation Training Devices (FSTDs) in Canada's general aviation (GA) sector, which, despite their longstanding adoption, remain underutilized. It also examines pilot perspectives on the potential of Augmented Reality (AR) technology as an assistive tool in GA pilot training. An online survey gathered views on FSTD use for routine flight operations and emergency training, as well as AR's potential to support learning. Responses from 197 participants show a strong interest (average rating above 4 on a 5-point scale) in incorporating FSTDs and AR technology into the GA pilot training framework. The findings suggest that immersive, technology-driven training environments have the potential to better address modern aviation demands and enhance pilot proficiency.
Keywords: Advanced training technologies; Augmented reality (AR); Flight simulator training device (FSTD); General aviation; Pilot perspectives.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Garg D, Patel B, Patel R, Jani R. Spatial Computing: Next Big Thing of Physical and Digital World. In: Kumar A, Senatore S, Gunjan VK, eds. ICDSMLA 2021. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Springer Nature, Cham; 2023:211–219. 10.1007/978-981-19-5936-3_20
-
- Nair MM, Tyagi AK. Chapter 11 - AI, IoT, blockchain, and cloud computing: The necessity of the future. In: Pandey R, Goundar S, Fatima S, eds. Distributed Computing to Blockchain. Academic Press; 2023:189–206. 10.1016/B978-0-323-96146-2.00001-2
-
- Tanwar, R., Bhatia, S., Sapra, V. & Ahuja, N. J. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: An Intelligent Perspective of Emerging Technologies (CRC Press, UK, 2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

