Interaction of STIL with FOXM1 regulates SF3A3 transcription in the hepatocellular carcinoma development
- PMID: 39825314
- PMCID: PMC11740530
- DOI: 10.1186/s13008-025-00142-4
Interaction of STIL with FOXM1 regulates SF3A3 transcription in the hepatocellular carcinoma development
Abstract
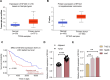
Background: Dysregulation of SF3A3 has been related to the development of many cancers. Here, we investigated the functional role of SF3A3 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
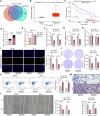
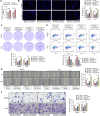
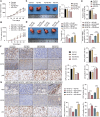
Methods: SF3A3 expression in HCC tissues and cell lines was examined using RT-qPCR. Changes in malignant behavior of HCC cells after downregulation of SF3A3 were assessed by EdU, colony formation, flow cytometry, wound healing, and Transwell invasion assays. Multiple datasets were combined to identify the upstream modifiers of SF3A3. The binding relationship between STIL and FOXM1 was explored by co-IP assay, and the effect of STIL and FOXM1 on the binding of FOXM1 at the SF3A3 promoter was detected by ChIP-qPCR assay. A xenograft tumor model was established to explore the changes of tumors in vivo, and the expression of Ki67, GPC3, and p53 in tumor tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry.
Results: SF3A3 and STIL were overexpressed in HCC tissues and cells, and downregulation of SF3A3 or STIL inhibited the malignant behavior of HCC cells by promoting the expression of p53. An interaction between STIL and FOXM1 regulated the SF3A3 expression in HCC cells. Knockdown of FOXM1 further enhanced the anti-tumor effects of STIL loss on HCC cells in vitro and in vivo, whereas SF3A3 overexpression overturned the impact of STIL loss on HCC cells in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that STIL/FOXM1 expedites HCC development by activating SF3A3, which highlights the importance of SF3A3 as a promising prognostic marker and therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: FOXM1; Hepatocellular carcinoma; P53; SF3A3; STIL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The research protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Qiqihar and conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients signed a written informed consent. All animal experiments performed were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Qiqihar and conducted in conformance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the NIH. Consent to participate: Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants. Consent for publication: All authors read the guidelines of the journal and agreed with consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circular RNA Circ-STIL Contributes to Cell Growth and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Regulating miR-345-5p/AQP3 Axis.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Jun;67(6):2269-2282. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07054-7. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 34231101
-
A novel HIF1α-STIL-FOXM1 axis regulates tumor metastasis.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Apr 1;29(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00807-0. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 35365182 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1-activated IGF2BP3 promotes cell malignant phenotypes and M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ferroptosis via stabilizing RRM2 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 May;480(5):3051-3066. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05170-2. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39630361
-
Sorafenib inhibits proliferation and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via up-regulation of p53 and suppressing FoxM1.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Feb;36(2):241-51. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.122. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25557114 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor FOXM1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma malignant progression through activation of the WNT pathway by binding to SETDB1.Tissue Cell. 2023 Oct;84:102186. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102186. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Tissue Cell. 2023. PMID: 37556918
Cited by
-
The oncogenic role of FOXM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanisms, clinical significance, and therapeutic potentials.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04144-5. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40266300 Review.
References
-
- Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):7. 10.1038/s41572-021-00245-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

