Potentially probiotic NPL 1334 strain of Enterococcus durans benefits rats with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 39825321
- PMCID: PMC11740586
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-024-00943-5
Potentially probiotic NPL 1334 strain of Enterococcus durans benefits rats with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
Purpose: To study the potential of a candidate probiotic strain belonging to the Enterococcus durans species in alleviating hypercholesterolemia and improving the microbial milieu of rat gut.
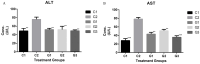
Methods: A previously isolated and characterized E. durans strain NPL 1334 was further screened in vitro for its bile salt hydrolyzation and cholesterol assimilation ability. An in vivo trial using diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats was conducted to evaluate the effects of the administered test probiotic strain on the animal's blood biochemical parameters such as total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipopolysaccharides (HDL), low-density lipopolysaccharides (LDL), triglycerides (TG), on body weight, oxidative stress markers, and its impact on intestinal and fecal microbiota as well as a histopathological examination of the test animal's livers.
Results: E. durans strain showed good bile salt hydrolyzing ability and ample cholesterol assimilation in vitro. Probiotic-fed hypercholesterolemic rats showed significantly lowered cholesterol, triglyceride and LDL levels. The body weight of probiotic-fed rats was reduced as compared to the control. E. durans also stimulated the growth of beneficial LAB in the intestine of experimental rats and did not harm the liver of the experimental rats.
Conclusion: E. durans can be a natural therapeutic alternative to manage diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and may eventually enhance anti-cholesterolemic therapies.
Keywords: Antioxidant potential; Enterococcus; Gut microbiota; Hypercholesterolemia; Probiotics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Animal research was done according to the Declaration of Helsinki, which gives guidelines for caring and using institutional laboratory animals for research. The Ethical and Biomedical Committee of the Department of Physiology, Government College University Faisalabad, reviewed and approved the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Probiotic properties of Enterococcus strains isolated from traditional naturally fermented cream in China.Microb Biotechnol. 2016 Nov;9(6):737-745. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12306. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Microb Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26200795 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing Probiotic Potential of Enterococcus Strains Isolated From Traditionally Fermented Chhurpi and Healthy Human Gut.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 16;13:909987. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.909987. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35783420 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Cholesterol-Lowering Mechanism of Enterococcus faecium Strain 132 and Lactobacillus paracasei Strain 201 in Hypercholesterolemia Rats.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 9;13(6):1982. doi: 10.3390/nu13061982. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34207558 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus fermentum FTDC 8312 combats hypercholesterolemia via alteration of gut microbiota.J Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 20;262:75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 19. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28935567
-
Hypocholesterolemic Effects of Probiotic Mixture on Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemic Rats.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 16;9(3):293. doi: 10.3390/nu9030293. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28300786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaretti A, Di Nunzio M, Pompei A, Raimondi S, Rossi M, Bordoni A. Antioxidant properties of potentially probiotic bacteria: in vitro and in vivo activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97:809–17. 10.1007/s00253-012-4241-7. - PubMed
-
- Aminlari L, Shekarforoush SS, Hosseinzadeh S, Nazifi S, Sajedianfard J, Eskandari MH. Effect of probiotics Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus plantarum on lipid profile and feces bacteria of rats fed cholesterol-enriched diet. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019;11:1163–71. 10.1007/s12602-018-9480-1. - PubMed
-
- Anwar H, Hussain G, Rasul A, Ali Shah SM, Naqvi SAR, Bukhari SA, Munir N. Potential role of probiotic species in ameliorating oxidative stress, effect on liver profile and hormones in male albino rat model. Eur J Inflamm. 2021;19:20587392211016119.
-
- Aziz G, Zaidi A, Tariq M. Compositional quality and possible gastrointestinal performance of marketed probiotic supplements. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2022;14(2):288–312. 10.1007/s12602-022-09931-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

