Molecular clustering on ctDNA improves the prognostic stratification of patients with DLBCL compared with ctDNA levels
- PMID: 39825831
- PMCID: PMC11999195
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014136
Molecular clustering on ctDNA improves the prognostic stratification of patients with DLBCL compared with ctDNA levels
Abstract
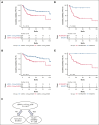
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels can help predict outcomes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but its integration with DLBCL molecular clusters remains unexplored. Using the LymphGen tool in 77 DLBCL cases with both ctDNA and tissue biopsy, a 95.8% concordance rate in molecular cluster assignment was observed, showing the reproducibility of molecular clustering on ctDNA. A multicenter, prospective cohort of 166 patients with newly diagnosed DLBCL was analyzed for ctDNA levels and molecular clusters using cancer personalized profiling by deep sequencing. Patients with ctDNA levels of <2.5 log10 haploid genome equivalents (hGE)/mL had a 4-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of 71.7% and 85.7%, respectively, compared with 50.3% and 61.0% for those with higher ctDNA levels (P = .0018 and P = .0017). Recursive partitioning showed that patients with ctDNA levels of ≥2.5 log10 hGE/mL were further stratified by clusters ST2/BN2. In this group, ST2/BN2 patients associated with a favorable outcome with a 4-year PFS and OS of 87.5% and 100%, respectively, compared to 38.0% and 47.1% for other clusters (P = .003 and P = .001). Combining ctDNA levels and ST2/BN2 clusters improved outcome prediction. Low-risk patients (n = 51), characterized by ctDNA levels of <2.5 log10 hGE/mL and/or BN2/ST2 cluster, had a 4-year PFS and OS of 75.3% and 87.8%, respectively. High-risk patients (n = 115), with ctDNA levels of ≥2.5 log10 hGE/mL and no BN2/ST2 cluster, had a 4-year PFS and OS of 38.0% and 47.1%, respectively. Adding cluster assignment to ctDNA levels improved the model's C statistics (0.63 vs 0.59 for PFS; 0.68 vs 0.63 for OS). Liquid biopsy thus provides a multilayered approach for outcome prediction in DLBCL.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403(6769):503–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

